Introduction
Understanding Insulators in Power Lines
Insulators are designed to prevent the unwanted flow of electricity, acting as barriers between conductive materials and their surroundings. In power lines, they support and separate conductors while withstanding harsh environmental conditions without compromising performance. The effectiveness of electrical insulators directly impacts the safety and reliability of transmission lines, making them indispensable in high voltage applications.
Importance of Insulators in Transmission Lines
The importance of insulators cannot be overstated; they ensure that electricity remains confined within its designated path while minimizing energy loss and preventing short circuits. By maintaining proper insulation, these components help protect both infrastructure and nearby communities from potential hazards associated with high voltage transmission. Furthermore, effective insulator design contributes to the longevity of power line systems, reducing maintenance costs over time.
Overview of Types of Insulators
There are several types of insulators used in power lines today, each offering unique benefits tailored to specific applications. Among these are glass electrical insulators known for their durability and transparency; porcelain insulators celebrated for their robustness; and composite insulators which combine materials for enhanced performance under extreme conditions. By exploring these various types of insulators, we gain insight into their individual roles within the broader context of electrical engineering.
Definition of Electrical Insulators

Electrical insulators are materials that prevent the flow of electric current, thus playing a crucial role in electrical wiring and power lines. These insulators ensure that electricity travels along designated paths without leaking into the environment, which is especially important in high voltage applications. By providing a barrier between conductive elements and their surroundings, electrical insulators maintain system efficiency and safety.
Characteristics of Electrical Insulators
One of the key characteristics of electrical insulators is their high resistance to electrical current, which allows them to withstand significant voltage levels without breaking down. This property is essential for ensuring that types of insulators can operate effectively in various environments, particularly where high voltage is involved. Additionally, good insulators are often resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, and UV radiation, making them durable choices for outdoor transmission lines.
Role in High Voltage Systems
In high voltage systems, electrical insulators serve as the backbone that supports and protects the infrastructure from potential hazards such as short circuits or power surges. They maintain safe distances between live wires and other conductive materials or structures while also minimizing energy loss during transmission. The reliability of these systems hinges on the performance of different types of insulators; any failure could lead to catastrophic consequences like outages or even accidents.
Common Materials Used
The most common materials used for making electrical insulators include glass, porcelain, and composite substances—each offering unique benefits tailored to specific applications in power lines. Glass electrical insulators are known for their excellent dielectric properties and durability under extreme conditions; they’re often seen on older transmission lines due to their longevity. On the other hand, porcelain has been a traditional choice because it can withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress; meanwhile, composite materials combine lightweight characteristics with superior performance against contamination and weathering effects.
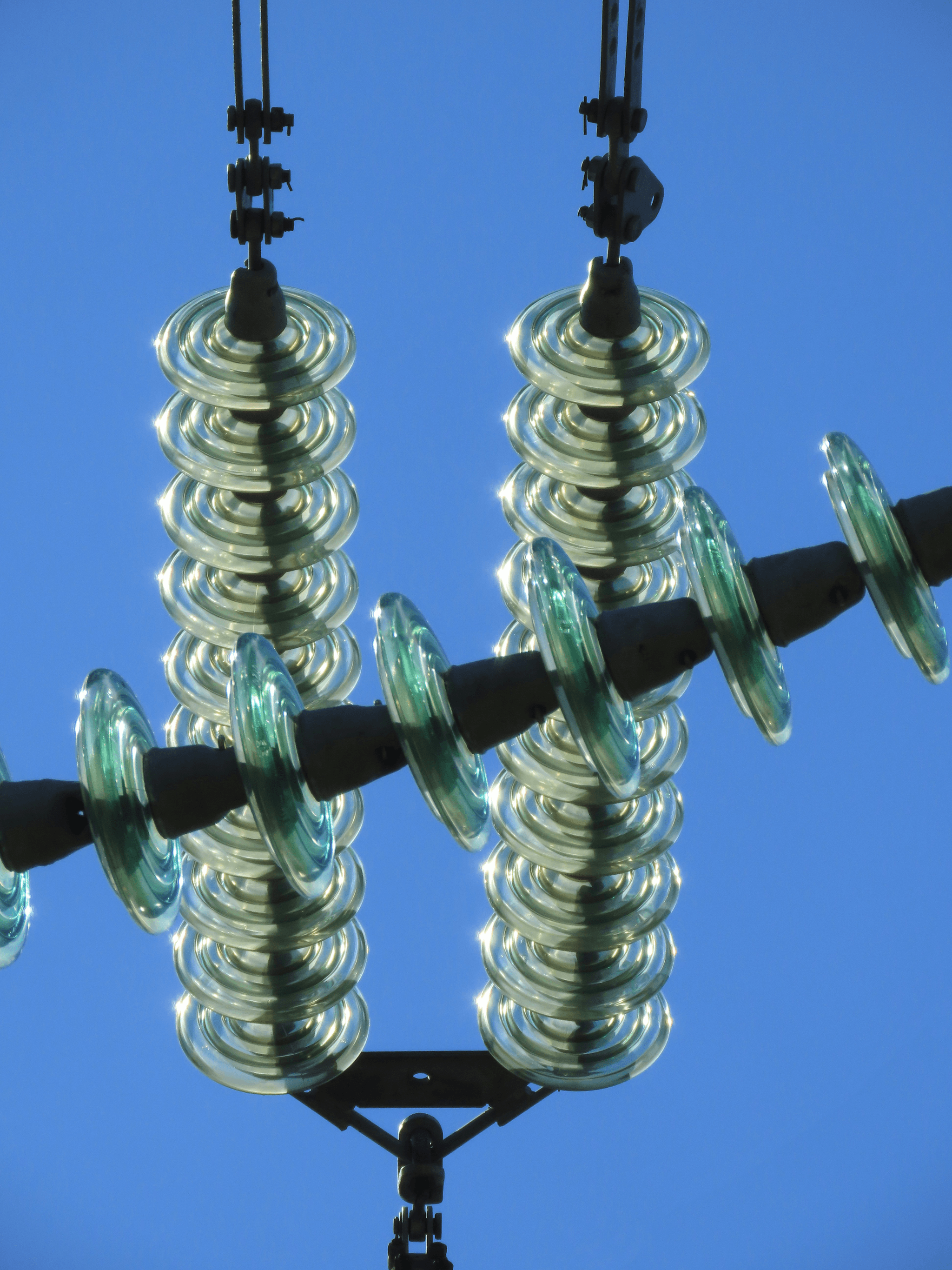
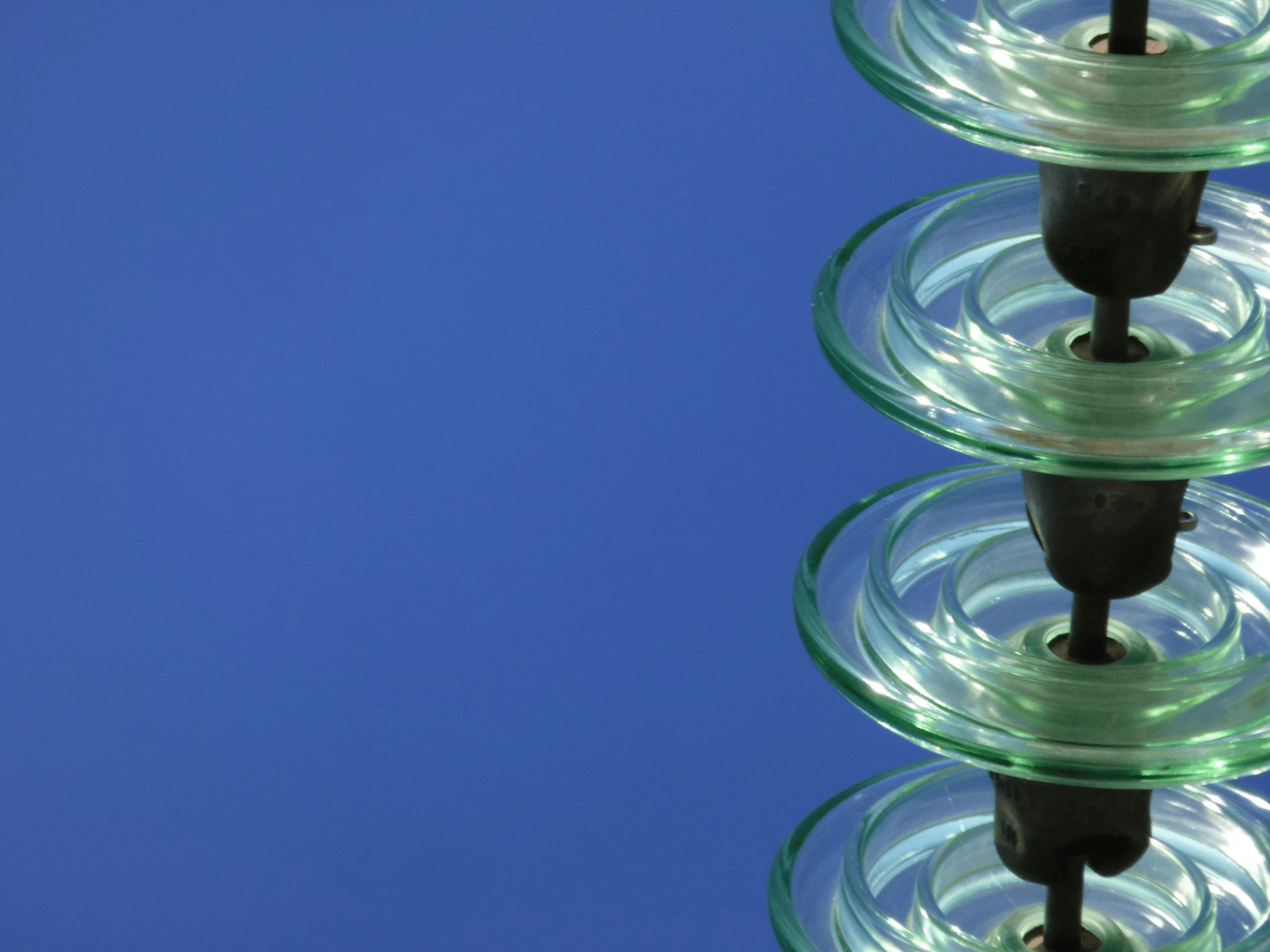
Glass Electrical Insulators

Glass electrical insulators have been a staple in the world of power lines for decades, and for good reason. Their unique properties make them an excellent choice for high voltage applications, providing reliable performance while withstanding the elements. In this section, we will explore the benefits of glass insulators, their various types, and how they are utilized in transmission lines.
Benefits of Glass Insulators
One of the standout benefits of glass insulators is their exceptional durability. Unlike some other types of insulators, glass can withstand extreme weather conditions without compromising its integrity. Additionally, glass electrical insulators are highly resistant to UV radiation and do not degrade over time as some organic materials might; this longevity makes them a cost-effective choice for utility companies looking to maintain their electrical wiring systems.
Another advantage is their superior electrical performance. Glass insulators have a low dielectric constant and high insulation resistance, which helps minimize energy loss in high voltage systems. This efficiency plays a vital role in ensuring that power lines operate smoothly without unnecessary interruptions or failures.
Lastly, glass insulators are also aesthetically pleasing due to their clear or colored designs that can blend well with natural surroundings. This aspect is particularly beneficial when considering public perception and environmental impact since visually appealing infrastructure can help mitigate opposition from local communities regarding new transmission line projects.
Types of Glass Electrical Insulators
When it comes to types of glass electrical insulators, there are several options available depending on the specific needs of power lines and transmission systems. The most common types include suspension insulators, pin-type insulators, and strain insulators; each serves a distinct purpose within the broader context of electrical wiring.
Suspension insulators are typically used in high voltage transmission lines where long spans between towers require robust support structures. These glass insulators hang from the line itself and help maintain tension while preventing any conductive material from bridging gaps that could lead to shorts or outages.
Pin-type insulators are another popular choice; these attach directly to poles or towers and provide stability for lower voltage applications or distribution networks. Strain insulators serve as anchors at points where cables experience significant tension due to wind or other forces—ensuring that wires remain securely fastened even under challenging conditions.
Applications in Transmission Lines
Glass electrical insulators find extensive applications across various transmission line setups due to their reliability and performance characteristics. They are particularly favored in overhead power lines where maintaining insulation integrity is critical for safety and efficiency at high voltages.
In addition to traditional overhead setups, these glass insulator designs have also been adapted for use in urban environments where space constraints may require innovative solutions—such as compact installations on existing infrastructure like buildings or bridges without sacrificing safety standards.
Moreover, advancements in manufacturing techniques have led to improved designs that enhance both mechanical strength and aesthetic appeal—allowing utilities to deploy modernized power lines while addressing community concerns about visual impact alongside functionality requirements associated with different types of electrical wiring systems.
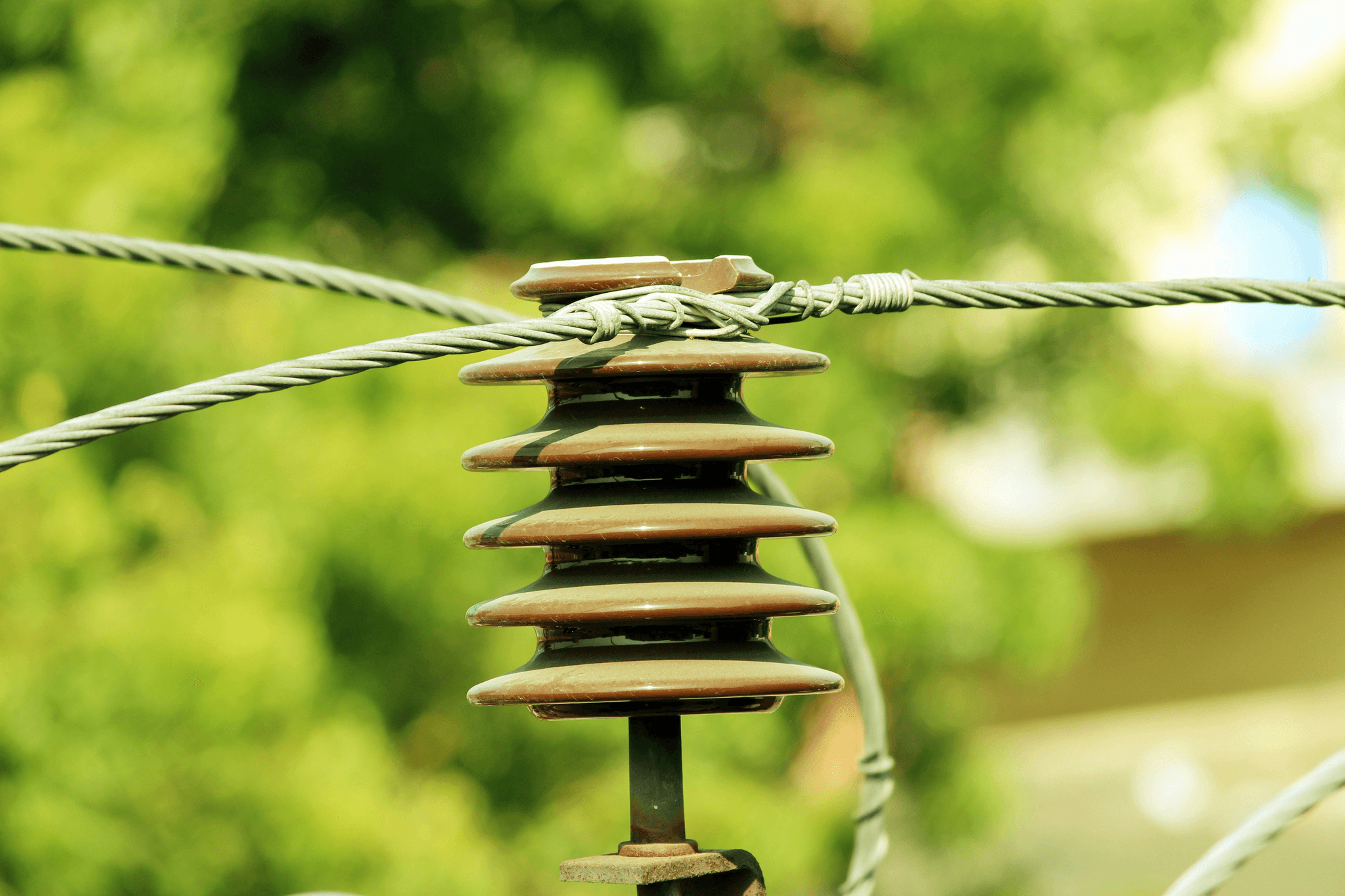
Porcelain Insulators

Porcelain insulators have long been a staple in the world of electrical wiring, particularly for power lines operating at high voltage. Known for their robust nature, these types of insulators offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice in many transmission line applications. Their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining electrical integrity sets porcelain insulators apart from other options like glass electrical insulators.
Advantages of Porcelain Insulators
One of the standout advantages of porcelain insulators is their exceptional mechanical strength, which allows them to endure significant stress without breaking. This durability makes them ideal for use in high voltage applications where reliability is paramount. Additionally, porcelain has excellent resistance to weathering and UV radiation, ensuring that these electrical insulators can maintain their performance over extended periods, even when exposed to the elements.
Another benefit is their inherent resistance to tracking and erosion, which are common issues faced by other types of insulators like glass insulators. This means that porcelain can maintain its insulating properties longer without requiring frequent maintenance or replacement. Furthermore, they are less prone to cracking under thermal stress compared to some alternatives, making them a reliable choice for various power line configurations.
Design and Durability
The design of porcelain insulators typically features a smooth surface that minimizes dirt accumulation—a crucial factor in maintaining effective insulation in transmission lines. Their robust structure not only contributes to their longevity but also allows for easy installation on overhead power lines without compromising safety or functionality. The classic design often includes an umbrella shape which helps shed water and debris effectively.
Durability is another hallmark of porcelain insulators; they can withstand extreme temperatures and resist mechanical impacts better than many other materials used in electrical wiring systems today. The firing process used during manufacturing creates a dense ceramic body that enhances its strength and longevity significantly compared to glass electrical insulators or composite options. This resilience makes porcelain an excellent choice for various environments—from urban settings with pollution challenges to rural areas facing harsh weather conditions.
Usage in Overhead Power Lines
Porcelain insulators are widely utilized in overhead power lines due to their reliability and performance under high voltage conditions. They serve as critical components that support conductors while preventing unwanted current leakage—ensuring safe transmission across vast distances without compromising efficiency or safety standards associated with electrical wiring systems. Their proven track record makes them a go-to option when designing new infrastructure or upgrading existing power line networks.
In addition to standard transmission lines, these types of insulators are also employed in substations and distribution systems where high voltage operations occur frequently. Their ability to handle heavy loads while resisting environmental factors ensures minimal downtime due to maintenance issues—an essential consideration for utility companies looking at cost-effective solutions over time. As renewable energy sources become more prevalent, the role of durable materials like porcelain will continue expanding as part of modern energy infrastructure strategies.
Composite Insulators
Composite insulators have carved out a significant niche in the world of electrical wiring and power lines, thanks to their unique blend of materials and innovative design. They typically consist of a core made from fiberglass or another composite material, which is then covered with a weather-resistant polymer. This combination not only enhances their mechanical strength but also provides excellent electrical insulation properties, making them suitable for high voltage applications.
Features of Composite Insulators
One standout feature of composite insulators is their lightweight nature, which makes them easier to transport and install compared to traditional glass electrical insulators or porcelain options. Additionally, they exhibit superior resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, pollution, and extreme temperatures. This durability means that composite insulators require less maintenance over time, ultimately reducing operational costs for utility companies managing extensive transmission line networks.
Comparison with Glass and Porcelain
When comparing composite insulators to glass and porcelain types of insulators, several key differences emerge. While glass electrical insulators are known for their transparency and aesthetic appeal, they can be heavier and more fragile than their composite counterparts. Porcelain insulators have long been favored for their robustness but may not offer the same level of flexibility in design or resistance to harsh conditions as composite types do; thus, each has its place in the grand scheme of electrical wiring.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
Composite insulators shine particularly bright when it comes to performance in extreme conditions such as heavy winds or icy weather—situations where traditional materials might falter. Their ability to withstand mechanical stress while maintaining excellent dielectric strength makes them ideal for high voltage applications across varied climates. As power lines stretch across diverse terrains globally, these modern marvels ensure reliable electricity delivery without compromising safety or efficiency.
Specialty Insulators by Spark Fittings

In the evolving landscape of electrical wiring, Spark Fittings has carved a niche by offering specialty insulators that meet the diverse demands of modern power lines. These products are designed to enhance performance in high voltage applications while ensuring safety and reliability. By focusing on innovative designs and materials, Spark Fittings provides solutions that address both current challenges and future needs in transmission line infrastructure.
Overview of Spark Fittings Products
Spark Fittings boasts an impressive array of specialty insulators tailored for various types of insulators used in high voltage systems. Their product line includes glass electrical insulators, porcelain options, and cutting-edge composite designs that cater to different environmental conditions and operational requirements. Each type is meticulously engineered to withstand the rigors of electrical wiring while providing optimal insulation performance in power lines.
Innovations in Insulator Manufacturing
The manufacturing process at Spark Fittings incorporates advanced technologies that push the boundaries of traditional electrical insulators. For instance, their glass insulators are not only aesthetically pleasing but also feature enhanced strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for long spans on transmission lines. Additionally, innovations such as improved surface treatments for porcelain insulators help reduce contamination effects, thereby increasing their lifespan and reliability under high voltage conditions.
Impact on Modern Power Line Infrastructure
The impact of specialty insulators from Spark Fittings on modern power line infrastructure cannot be overstated. By integrating these advanced types of insulators into existing systems, utilities can achieve greater efficiency and reduce maintenance costs over time. Moreover, with a growing emphasis on renewable energy systems, these electrical insulators play a crucial role in facilitating the transition to greener technologies by ensuring safe and reliable energy transmission.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the various types of insulators is crucial for anyone involved in electrical wiring and power line infrastructure. From glass electrical insulators to porcelain and composite options, each type offers distinct advantages suited to different applications in high voltage systems. These insulators not only ensure safety and reliability but also play a pivotal role in the efficiency of transmission lines.
Key Takeaways on Insulator Types
The landscape of electrical insulators is diverse, with glass insulators being celebrated for their durability and transparency, while porcelain insulators are known for their strength and longevity. Composite insulators have emerged as a modern alternative, providing flexibility in extreme conditions where traditional materials may falter. Each type of insulator contributes uniquely to the overall performance of power lines, making it essential to choose wisely based on specific needs.
Future Trends in Electrical Insulators
Looking ahead, we can expect innovations in electrical insulator design that prioritize sustainability and efficiency. The integration of smart technologies into power lines will likely lead to more advanced types of insulators that monitor performance and predict maintenance needs proactively. Furthermore, as renewable energy systems gain traction, the demand for specialized electrical insulators capable of handling varying loads will increase significantly.
The Role of Insulators in Renewable Energy Systems
Insulators are set to become even more critical as we transition towards renewable energy systems like wind and solar power. These systems require reliable transmission lines capable of managing high voltage outputs while maintaining safety standards—something that robust glass electrical insulators can provide effectively. As we embrace cleaner energy solutions, understanding the role and functionality of various types of insulators will be key to building a resilient energy infrastructure.

