Introduction
Insulators play a critical role in electrical systems, acting as barriers that prevent unwanted current flow and ensuring safety and efficiency. Understanding insulator materials is essential for engineers and technicians working with power systems, as the choice of insulator can significantly affect performance. Among the various types of insulators, porcelain and glass stand out due to their unique properties and applications.
Understanding Insulator Materials
When discussing insulator materials, it's vital to recognize the different types available, particularly porcelain insulator types and glass insulators. Porcelain is a ceramic material known for its durability and resistance to environmental factors, while glass offers excellent transparency for monitoring purposes. Each material has its own set of advantages that cater to specific needs in power transmission.
Importance of Insulator Types in Power Systems
The importance of selecting the right insulator type cannot be overstated; it impacts not only the reliability of power delivery but also safety measures within electrical systems. In high-voltage applications, understanding how to identify porcelain insulators or what are four types of insulators can be crucial for maintaining system integrity. The choice between porcelain and glass affects everything from installation costs to maintenance schedules.
Overview of Porcelain and Glass Insulators
Porcelain insulators have been a staple in electrical engineering for decades, valued for their strength and longevity—often boasting a life expectancy that can exceed 50 years under optimal conditions. On the other hand, glass insulators have gained popularity due to their ease of inspection and resistance to moisture accumulation. As we delve deeper into these materials' compositions, manufacturing processes, strengths, and weaknesses, it becomes clear why understanding porcelain insulator manufacturers is essential for making informed decisions about insulation technology.
Composition of Porcelain Insulators

Porcelain insulators are a staple in the world of electrical power systems, known for their durability and excellent insulating properties. They come in various forms, each tailored for specific applications, making it essential to understand the different porcelain insulator types available. This section explores the intricacies of porcelain insulators, from their composition to their manufacturing processes and advantages.
What Are Porcelain Insulator Types?
Porcelain insulator types can be broadly categorized into several groups based on their design and application. The most common types include suspension insulators, pin-type insulators, post insulators, and strain insulators. Each type serves a distinct purpose; for example, suspension insulators are often used in high-voltage transmission lines, while pin-type insulators are typically found on utility poles.
Understanding how to identify porcelain insulators is crucial for selecting the right type for your project. Look for characteristics such as shape, size, and mounting features that differentiate one type from another. Additionally, recognizing these traits can help you determine what are the different types of ceramic insulators available in the market.
Manufacturing Process of Porcelain Insulators
The manufacturing process of porcelain insulators involves several meticulous steps to ensure high-quality products that meet industry standards. First, raw materials like kaolin clay, feldspar, and quartz are blended to create a homogenous mixture suitable for forming the desired shapes. This mixture is then shaped into various forms using molds before being fired at high temperatures in kilns to achieve strength and durability.
Once fired, porcelain undergoes glazing processes that enhance its insulation properties while providing an aesthetically pleasing finish. The final product is rigorously tested to ensure it meets electrical performance requirements before being distributed by notable porcelain insulator manufacturers worldwide. These manufacturers play a vital role in advancing technology related to porcelain insulation through innovations and improved production techniques.
Advantages of Porcelain in Insulation
Porcelain offers numerous advantages when used as an insulating material in power systems—chief among them being its excellent dielectric strength and resistance to environmental factors like moisture and UV radiation. This makes porcelain particularly well-suited for outdoor applications where exposure to harsh conditions is inevitable; thus contributing significantly to what is the life expectancy of a porcelain insulator.
Moreover, due to its robust nature and resistance to thermal shock, porcelain can withstand extreme temperature variations without degrading over time—an essential characteristic that enhances its longevity compared with other materials like glass or plastic alternatives. In summary, understanding the strengths of different porcelain insulator types can help engineers make informed choices when designing power systems that require reliable insulation solutions.
Composition of Glass Insulators

Glass insulators have carved a niche in the world of electrical engineering, thanks to their unique properties and versatile applications. Unlike porcelain insulator types, glass insulators are often favored for their aesthetic appeal and transparency, allowing for easy visual inspection. This section will delve into how these remarkable components are made, the various types available, and their inherent strengths.
How Are Glass Insulators Made?
The manufacturing process of glass insulators is both intricate and fascinating. Initially, raw materials such as silica sand, soda ash, and limestone are mixed together to create a molten glass mixture at high temperatures. Once melted, this mixture is shaped into the desired form through techniques like blowing or pressing before being cooled down gradually to ensure durability—a method that contrasts with the processes used for porcelain insulator manufacturers.
Quality control is paramount during production; each glass insulator must meet stringent standards to ensure optimal performance in power systems. After shaping, they undergo annealing—a slow cooling process that enhances strength and reduces internal stresses—making them highly reliable under varying environmental conditions. This attention to detail results in robust products that can withstand the test of time.
Common Glass Insulator Types
When it comes to identifying glass insulator types, several common varieties stand out in power systems today. Among these are suspension insulators designed for overhead lines; they hang from transmission towers and support conductors while preventing electrical leakage. Another type includes pin-type insulators which attach directly to poles and provide stability for lower voltage lines.
Additionally, there are strain insulators used in areas where wires experience tension due to wind or weight—these help maintain line integrity under stress. Each type serves a specific purpose within the electrical grid and showcases how diverse insulation solutions can be when compared with porcelain options like those found among different types of ceramic insulators.
Strengths of Glass as an Insulator
Glass offers several advantages that make it an attractive choice over traditional porcelain materials used in power systems. One significant strength is its superior dielectric properties; glass has excellent electrical insulating capabilities which help prevent energy loss during transmission—this aspect often raises questions about what is the life expectancy of a porcelain insulator versus its glass counterpart.
Moreover, glass is inherently resistant to UV radiation and weathering effects such as moisture absorption or chemical degradation—factors that can compromise other materials over time. Its transparency allows engineers to easily spot cracks or defects during routine inspections—an essential feature not typically available with opaque porcelain insulator types.
Performance Comparison
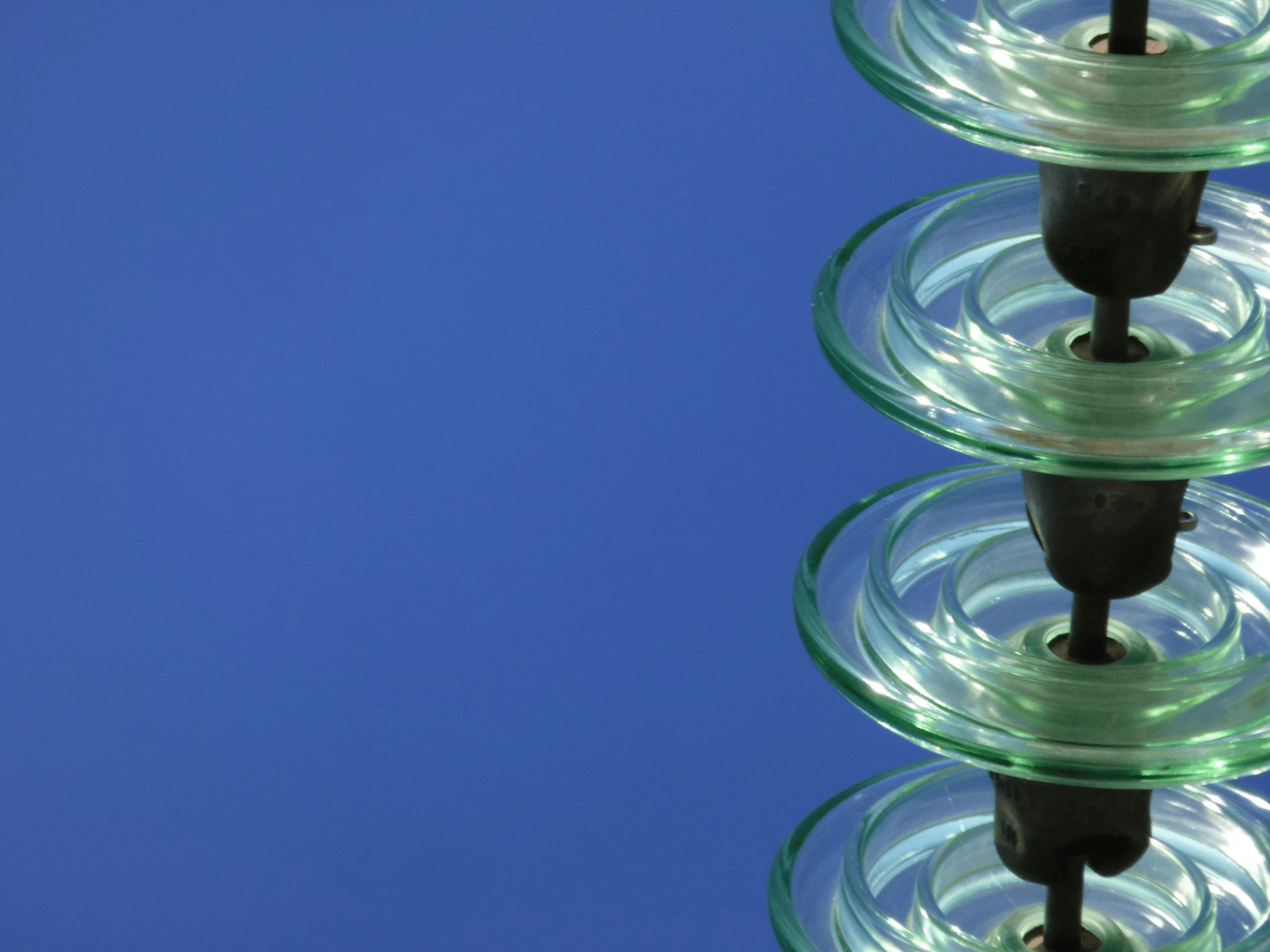

When it comes to the performance of insulators, both porcelain and glass have their unique strengths and weaknesses. Understanding how these materials stack up against each other is essential for making informed decisions in power system applications. This section will delve into the electrical properties, weather resistance, durability, and life expectancy of porcelain insulators compared to their glass counterparts.
Electrical Properties of Porcelain vs Glass
Electrical properties are a crucial factor when comparing porcelain insulator types with glass insulators. Porcelain typically exhibits excellent dielectric strength, making it highly effective in preventing electrical leakage. Glass, on the other hand, has superior transparency to electric fields but can be more susceptible to cracking under high-stress conditions.
Both materials serve well in high-voltage applications; however, the choice between them often boils down to specific project requirements. For instance, knowing how to identify porcelain insulators can help engineers select the right type based on environmental conditions and electrical demands. Ultimately, understanding what are four types of insulators—ceramic (porcelain), glass, composite, and polymer—can guide professionals in selecting the most suitable option for their needs.
Weather Resistance and Durability
Weather resistance is another significant aspect where porcelain and glass differ substantially. Porcelain insulator manufacturers have long touted the material's ability to withstand extreme temperatures without degrading its performance or structural integrity. Conversely, while glass offers good weather resistance as well, it can be more vulnerable to mechanical stress such as hail or heavy winds.
The durability of these materials also plays a pivotal role in their lifespan and maintenance costs over time. In harsh environments where exposure to moisture or pollutants is common, porcelain tends to outperform glass due to its non-porous nature that resists corrosion better than many other materials—including certain types of ceramic insulators that may absorb water over time. Thus, understanding how weather impacts different types of insulation is vital for long-term planning.
Life Expectancy of Porcelain Insulators
What is the life expectancy of a porcelain insulator? Generally speaking, these robust components boast impressive longevity—often exceeding 30 years when properly maintained! Their resilience against environmental factors contributes significantly to this extended lifespan compared with some glass alternatives which may require replacement sooner due to wear or damage.
Moreover, regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs or failures down the line—making proper maintenance essential for maximizing life expectancy across all porcelain insulator types used in various applications today! With advancements from leading manufacturers continually improving designs and materials used in production processes as well—it’s no wonder why engineers often lean toward porcelain options when longevity is paramount.
Identifying Insulator Types
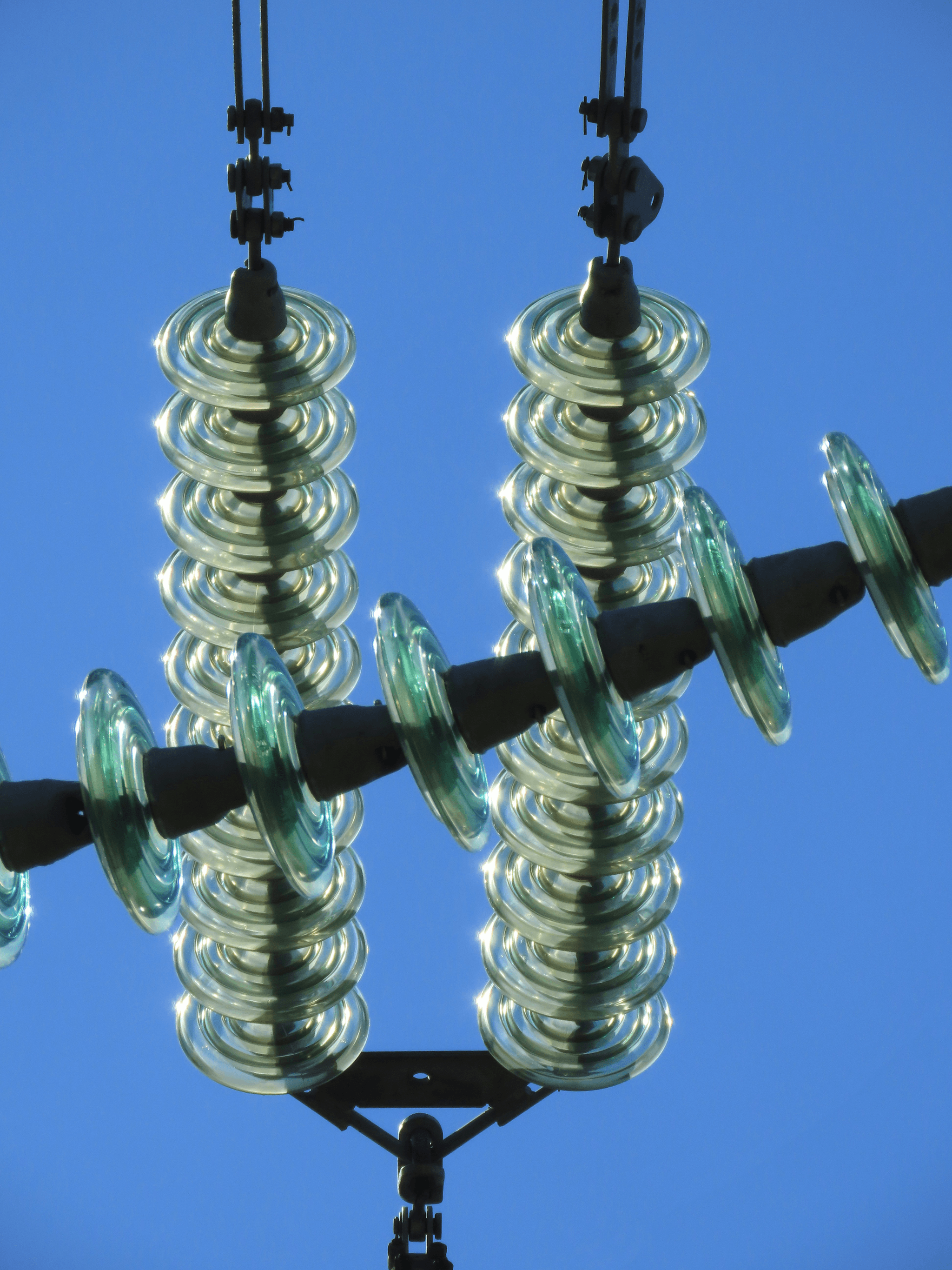
Identifying different insulator types is crucial for ensuring the reliability and safety of power systems. Among these, porcelain insulators hold a significant place due to their durability and effectiveness. This section will guide you through recognizing porcelain insulator types, exploring the four main categories of insulators, and highlighting visual cues that differentiate porcelain from glass.
How to Identify Porcelain Insulators?
To identify porcelain insulators, start by examining their physical characteristics. Porcelain insulator types typically exhibit a smooth, glossy surface with a white or light-colored finish, which is indicative of high-quality ceramic materials used in their production. Additionally, look for markings or stamps on the base that may indicate the manufacturer or specific type; many reputable porcelain insulator manufacturers include identifiable logos.
Another key feature to consider is the shape of the insulator. Porcelain insulators often have distinct profiles, such as disc shapes or pin-type configurations designed for various applications in power lines. Lastly, check for any signs of wear or damage; a well-maintained porcelain insulator should show minimal signs of degradation over time due to its impressive life expectancy.
What Are Four Types of Insulators?
When discussing what are four types of insulators, we primarily refer to pin-type, suspension-type, strain-type, and shackle-type insulators. Pin-type porcelain insulators are mounted directly onto poles and are commonly used in low-voltage applications; they resemble small discs with a single mounting point at the bottom. Suspension-type insulators hang from overhead lines and are typically used in high-voltage scenarios where long spans between towers exist.
Strain-type insulators are designed to withstand tension forces when supporting wires under stress; they usually have an elongated shape that allows them to absorb these forces effectively. On the other hand, shackle-type insulators are more compact and often utilized in secondary distribution networks where space is limited but still require reliable insulation against electrical discharge.
Visual Clues: Porcelain vs Glass
When distinguishing between porcelain and glass insulation materials visually, there are several clues that can help you make an accurate identification. First off, while both materials can be shiny and translucent under certain lighting conditions, glass typically has more color variations—ranging from clear to greenish hues—whereas most porcelain remains consistently white or light-colored due to its ceramic composition.
Another visual indicator is weight; generally speaking, porcelain is denser than glass when comparing similar sizes of each type of insulation material. Furthermore, examine any visible manufacturing seams: glass might display smoother edges due to its molding process compared to the sometimes rougher edges found on some porcelain designs.
Leading Manufacturers and Innovations

The landscape of insulator manufacturing is continuously evolving, with numerous manufacturers pushing the boundaries of technology and design. Porcelain insulator types have long been a staple in power systems, but innovation is breathing new life into their production and application. Understanding the key players in this field can provide insights into the reliability and effectiveness of different insulator types.
Notable Porcelain Insulator Manufacturers
Several notable porcelain insulator manufacturers have made significant contributions to the industry. Companies like Siemens, GE, and Hubbell are recognized for their high-quality porcelain insulators that meet stringent safety standards. These manufacturers not only produce various porcelain insulator types but also invest heavily in research and development to enhance performance and durability.
In addition to these giants, smaller companies are emerging with specialized offerings that cater to niche markets or unique applications. As competition increases, manufacturers are focusing on innovative designs that improve weather resistance and electrical performance. This evolution reflects a broader trend toward sustainability in manufacturing processes while maintaining high standards for quality.
Spark Fittings and Their Role
Spark fittings play an essential role in ensuring the effective functioning of porcelain insulators within power systems. These fittings connect wires securely while allowing for thermal expansion without compromising electrical integrity. Properly designed spark fittings contribute significantly to the overall longevity of porcelain insulators by minimizing stress at connection points.
Understanding how to identify porcelain insulators often includes recognizing compatible spark fittings that enhance their functionality. The right spark fitting can prevent failures caused by environmental factors such as moisture or temperature fluctuations, ultimately extending what is the life expectancy of a porcelain insulator? By integrating advanced materials into spark fitting designs, manufacturers can further boost durability and performance.
Emerging Trends in Insulator Technology
Emerging trends in insulation technology highlight a growing interest in hybrid materials that combine the best properties of both glass and ceramic components. Research is underway to develop new composite materials that may outperform traditional porcelain insulator types while addressing common concerns about weight and fragility associated with glass options.
Additionally, smart technology integration is becoming more prevalent within insulation systems, enabling real-time monitoring of electrical properties such as voltage levels or potential faults. This innovation allows for proactive maintenance strategies that could revolutionize how we assess what are four types of insulators used today—ensuring optimal performance across various applications.
As we look ahead at advancements in manufacturing techniques combined with innovative designs, it’s clear that both established players and newcomers will continue shaping the future landscape of insulation technology.
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between porcelain and glass insulators hinges on several key differences that can significantly impact their performance in power systems. Porcelain insulator types are renowned for their robust durability and resistance to environmental factors, while glass insulators offer excellent visibility and ease of inspection. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed decisions regarding insulation materials.
Key Differences Between Porcelain and Glass
When we delve into the specifics of porcelain insulator types versus glass, it's clear that both materials have unique strengths. For instance, porcelain typically has a longer life expectancy than many glass alternatives, often lasting decades under optimal conditions. However, glass insulators can be more resistant to certain types of mechanical stress and are easier to spot for maintenance checks—an essential factor when considering how to identify porcelain insulators.
Choosing the Right Insulator for Projects
Selecting the right type of insulator for your project requires careful consideration of various factors including environmental conditions, electrical demands, and budget constraints. If you're dealing with high-voltage lines in a harsh climate, you might lean toward specific porcelain insulator manufacturers known for their reliability and longevity. Conversely, if visibility during inspections is paramount or if you need to understand what are four types of insulators available in the market today, glass may be your best bet.
Final Thoughts on Insulator Selection
Ultimately, choosing between porcelain and glass comes down to understanding your specific needs and how each material meets them. The different types of ceramic insulators also play a role in this decision-making process; knowing what is available can guide you toward the most suitable option for your applications. Whether you're drawn to the durability of porcelain or the transparency of glass, informed choices lead to better outcomes in any electrical project.

