Introduction
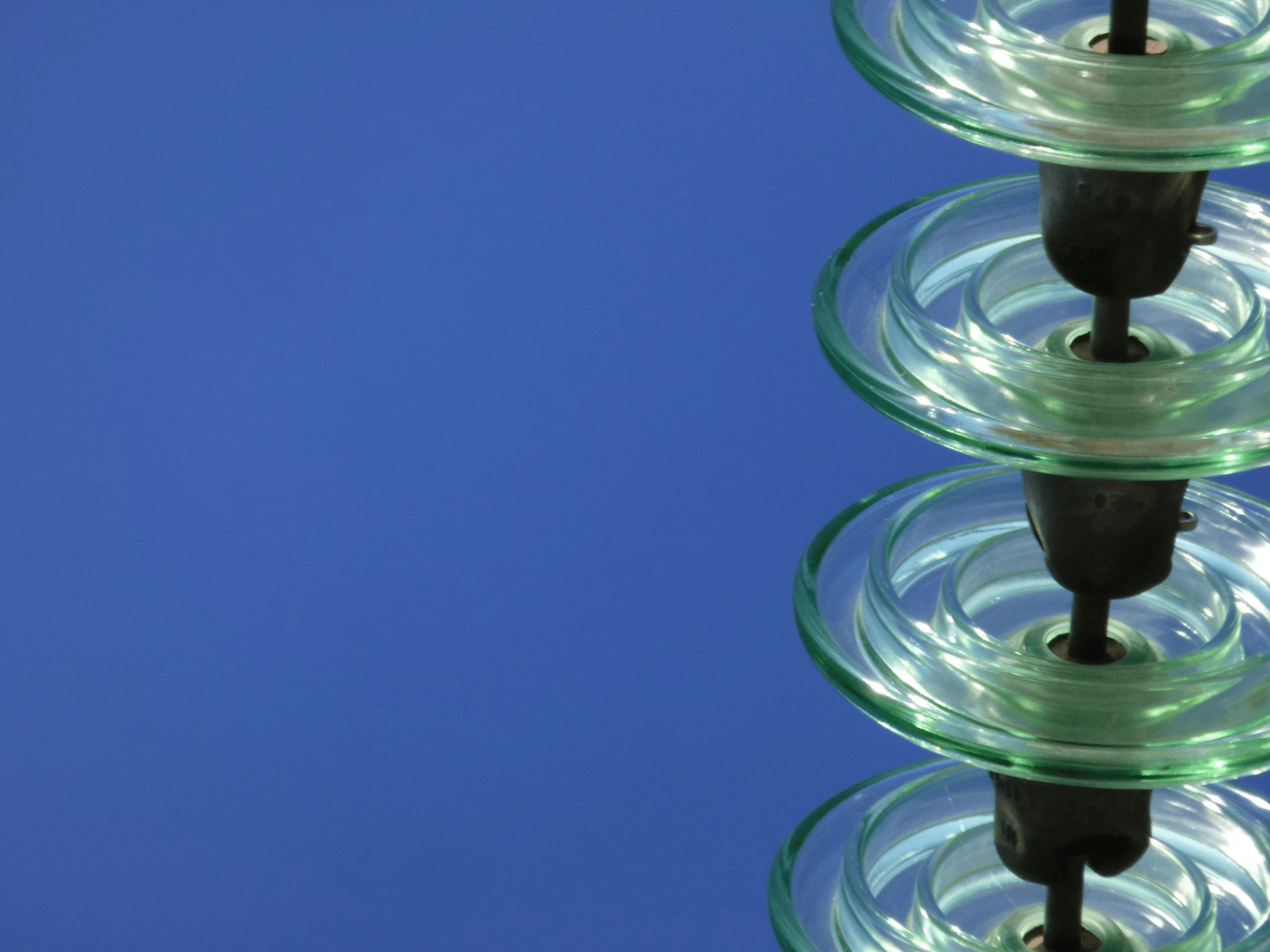

In the realm of electrical engineering, understanding transmission line insulators is crucial for ensuring efficient and safe power distribution. These unsung heroes play a vital role in keeping the integrity of our electrical systems intact, allowing electricity to travel long distances without interruption. But what are transmission line insulators? This introduction will shed light on their significance and the various types available.
Understanding Transmission Line Insulators
Transmission line insulators are devices that support and separate electrical conductors while preventing unwanted flow of current to the ground or other structures. They provide mechanical support and insulation, ensuring that high-voltage lines remain securely suspended above the ground. Without these essential components, our electrical grid would face numerous challenges, including short circuits and power outages.
Importance of Selecting the Right Insulator
Selecting the right insulator is not just a matter of preference; it’s a necessity for operational efficiency and safety in any electrical system. The choice can significantly influence performance, lifespan, and maintenance needs of transmission lines. As we explore questions like What are the four types of insulators used in overhead transmission lines? or What are 5 good insulators?, it becomes clear that informed decisions lead to better outcomes in energy distribution.
Overview of Types of Insulators
There are several types of insulators tailored for various applications within overhead transmission lines. Each type serves specific functions based on environmental conditions, voltage levels, and installation requirements. From suspension to strain insulators, understanding their distinctions paves the way for effective implementation in both traditional power grids and modern railway systems—prompting inquiries like Which insulator is used in a railway line?
What are Transmission Line Insulators?
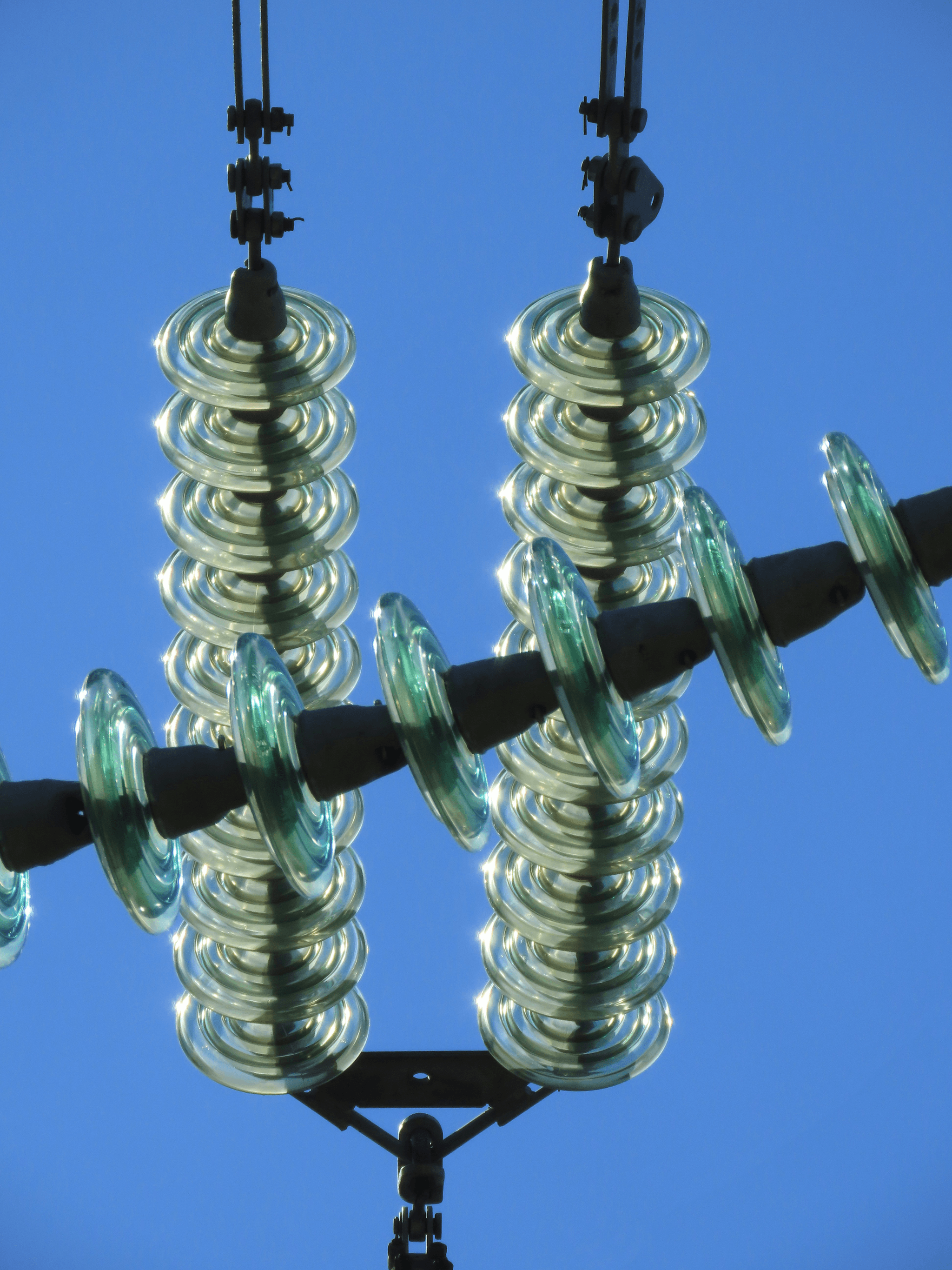
Transmission line insulators are crucial components in the electrical transmission system, ensuring that electricity flows safely and efficiently from one point to another. They serve as barriers that prevent electrical current from leaking to the ground or surrounding structures, thereby maintaining the integrity of the power supply. So, what are transmission line insulators? Simply put, they keep the wires suspended and insulated from other conductive materials.
Definition and Functionality
Transmission line insulators are devices designed to support overhead power lines while preventing unwanted electrical conduction. They function by providing electrical insulation between live wires and supporting structures such as towers or poles. This insulation is vital for maintaining safe distances between energized conductors and other objects, ensuring safety for both equipment and personnel.
Role in Electrical Transmission
In the realm of electrical transmission, these insulators play a pivotal role by facilitating efficient energy transfer while minimizing losses due to leakage currents. They help maintain voltage levels across long distances, which is essential for delivering electricity from generation sites to consumers without significant drops in quality or quantity. Additionally, transmission line insulators protect infrastructure from environmental factors like moisture, pollution, and temperature fluctuations that could compromise performance.
Key Characteristics
When considering types of insulators in transmission lines, several key characteristics come into play: mechanical strength, dielectric strength, weather resistance, and thermal stability are all important factors that define their performance. A good insulator should withstand physical stress while effectively resisting electrical breakdown under high voltage conditions. Furthermore, modern materials used in manufacturing these insulators often enhance durability against environmental degradation—making them reliable over time.
What are the Four Types of Insulators Used in Overhead Transmission Lines?

Suspension Insulators
Suspension insulators are typically used to support overhead conductors and keep them suspended from towers or poles. They consist of multiple discs made from materials like glass or porcelain, which are connected in series to increase their voltage handling capacity. The design allows for flexibility, accommodating movement caused by wind or temperature changes, making them essential for long spans between supports.
Strain Insulators
Strain insulators come into play when there’s a need to handle tension in the line, particularly at points where cables change direction or terminate. These insulators are designed to absorb stress while maintaining electrical insulation between the conductor and its supporting structure. They're crucial for ensuring that forces from wind or ice do not compromise the integrity of transmission line insulators.
Pin Insulators
Pin insulators are often used on lower voltage lines and attach directly to utility poles via a pin at their base. They provide a simple yet effective means of insulating conductors while allowing for easy installation and replacement when needed. While they may seem straightforward, pin insulators play an important role in maintaining safety by preventing electrical leakage down the pole.
Shackle Insulators
Shackle insulators serve as a versatile option often found in situations requiring horizontal support for conductors, such as at corners or changes in elevation along transmission lines. Their design allows them to be mounted on cross arms or directly onto poles, providing solid insulation while also supporting mechanical loads effectively. With their robust construction, shackle insulators contribute significantly to ensuring that transmission line insulators function optimally under various conditions.
What are 5 Good Insulators?

Glass Insulators
Glass insulators have been a staple in the industry for decades, known for their excellent electrical properties and durability. They are highly resistant to environmental factors such as UV radiation and moisture, making them ideal for outdoor use in various climates. Additionally, glass insulators provide a unique aesthetic appeal with their transparent appearance, allowing for easy visual inspection of any damage or defects.
Porcelain Insulators
Porcelain insulators are another classic choice when discussing what are transmission line insulators. Renowned for their high dielectric strength and mechanical stability, these ceramic-based insulators can withstand extreme weather conditions without compromising performance. Their inherent resistance to corrosion makes porcelain an excellent long-term investment for overhead transmission lines.
Composite Insulators
Composite insulators represent a modern evolution in insulation technology, combining materials like fiberglass with silicone rubber or polymeric compounds. These lightweight yet robust options offer superior performance in terms of pollution resistance and hydrophobicity compared to traditional materials. As we consider what are 5 good insulators, composite designs continue to gain traction due to their enhanced flexibility and reduced maintenance needs.
Silicone Rubber Insulators
Silicone rubber insulators have carved out a niche within the market due to their exceptional performance under harsh conditions. These flexible materials can endure temperature fluctuations while maintaining excellent insulating properties—perfect for regions experiencing extreme weather changes! Furthermore, silicone rubber's self-cleaning capabilities minimize maintenance efforts on transmission line insulators significantly.
Polymeric Insulators
Polymeric insulators round out our list as one of the top choices in insulation technology today. Made from advanced synthetic materials, they provide lightweight solutions without sacrificing strength or durability—ideal when considering types of insulators in transmission lines! Their ability to resist tracking and erosion makes polymeric options particularly beneficial for areas prone to heavy pollution or salt exposure.
Which Insulator is Used in a Railway Line?

Unlike traditional transmission line insulators, which are primarily designed for high-voltage power lines, railway insulators must contend with unique challenges including vibration, moisture, and varying loads. This section will delve into the specific insulation needs of railways and how they differ from standard transmission line applications.
Overview of Railway Insulation Needs
Railway systems require insulators that can withstand not only electrical stresses but also mechanical forces due to constant movement and vibrations from trains. These insulators must maintain their integrity under various weather conditions while providing reliable electrical isolation to prevent short circuits or failures. Given these demands, understanding what are transmission line insulators becomes essential; however, railway applications often call for specialized designs that cater specifically to their operational environment.
In addition to mechanical durability, railway insulation must also support efficient energy transfer without compromising safety standards. This means selecting materials that can handle both thermal expansion and contraction as well as resist degradation over time. Thus, when discussing which insulator is used in a railway line, it’s clear that the focus shifts towards materials that balance strength with effective insulation properties.
Comparison of Insulator Types for Railways
When comparing types of insulators in transmission lines with those utilized in railways, several factors come into play such as load capacity and environmental resistance. Common types like suspension and strain insulators may not be suitable due to their design being tailored for static overhead lines rather than dynamic rail environments. Instead, pin and composite insulators often take precedence because they offer better performance under the unique stresses found in railway applications.
Among the four types of insulators used in overhead transmission lines—suspension, strain, pin, and shackle—pin insulators are particularly favored for their compact size and ease of installation on poles along tracks. Composite materials are increasingly being adopted as they provide lightweight solutions with excellent resistance to weathering and pollution—a key consideration for rail systems exposed to diverse climates. Thus, understanding what are 5 good insulators helps streamline choices when determining which type works best for specific railway needs.
Spark Fittings' Role in Railway Insulators
Spark fittings play a pivotal role in enhancing the effectiveness of railway insulation by providing additional safety measures against electrical discharges or surges that might occur during operation. These fittings ensure that any stray currents do not compromise system integrity or endanger personnel working near tracks or stations. In this context, spark fittings complement traditional transmission line insulators by offering an extra layer of protection against unforeseen electrical events.
The integration of spark fittings within railway systems illustrates how innovative approaches can improve upon existing designs used in overhead power lines while addressing unique challenges faced by rail networks today. By harnessing advancements from various fields—including those related to what are transmission line insulators—railway engineers can develop solutions tailored specifically for their infrastructure requirements without sacrificing quality or reliability.
In conclusion, while there may be similarities between types of insulation used across different sectors like power distribution versus rail transport; understanding each application’s distinct needs is vital for optimal performance outcomes moving forward.
Types of Insulators in Transmission Lines

When it comes to transmission line insulators, understanding their various applications is crucial for ensuring effective electrical transmission. These insulators serve as a barrier between live wires and the supporting structures, preventing unwanted current flow while maintaining structural integrity under various environmental conditions. The right choice of insulator can significantly impact the efficiency and reliability of power distribution systems.
Overview of Insulator Applications
Transmission line insulators are deployed in a variety of scenarios, each tailored to specific needs within electrical infrastructure. For overhead transmission lines, different types of insulators, such as suspension and strain insulators, play key roles in supporting conductors while withstanding mechanical stress and environmental factors like wind and ice. Additionally, the selection of insulation material—be it glass or porcelain—depends on factors like voltage levels and local weather conditions.
In railway systems, specialized types of insulators are used to ensure safe operation under high-frequency electrical environments. These applications highlight the importance of selecting appropriate insulator types based on their intended use—whether for overhead lines or railways—to optimize performance and safety. Ultimately, understanding what are transmission line insulators helps engineers make informed decisions that enhance system reliability.
Selection Criteria for Insulators
Choosing the right type among the four types of insulators used in overhead transmission lines requires careful consideration of several factors. First off is voltage rating; higher voltages typically necessitate more robust materials to prevent breakdowns. Next, environmental conditions play a pivotal role; regions prone to heavy pollution may require composite or silicone rubber insulators due to their superior hydrophobic properties.
Mechanical strength also cannot be overlooked when assessing which insulator is used in a railway line versus traditional power lines; railway applications often face unique stresses from dynamic loads that demand specialized designs. Finally, cost-effectiveness must be factored into any decision-making process regarding types of insulators in transmission lines; balancing initial investment with long-term maintenance expenses is vital for sustainable operations.
Future Trends in Insulator Technology
The landscape for transmission line insulators is rapidly evolving with advancements in technology paving the way for innovative solutions. Emerging materials such as advanced polymers promise enhanced durability while reducing weight—a critical factor for both overhead power lines and railways alike. Furthermore, smart insulation technologies that incorporate sensors could revolutionize how we monitor performance and predict failures before they occur.
Sustainability trends are also influencing future designs; manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials that maintain high performance without compromising safety standards associated with traditional options like glass or porcelain insulation products. As we look ahead at what are 5 good insulators for modern applications, it's clear that innovation will continue driving improvements across all aspects related to transmission line insulation.
Conclusion
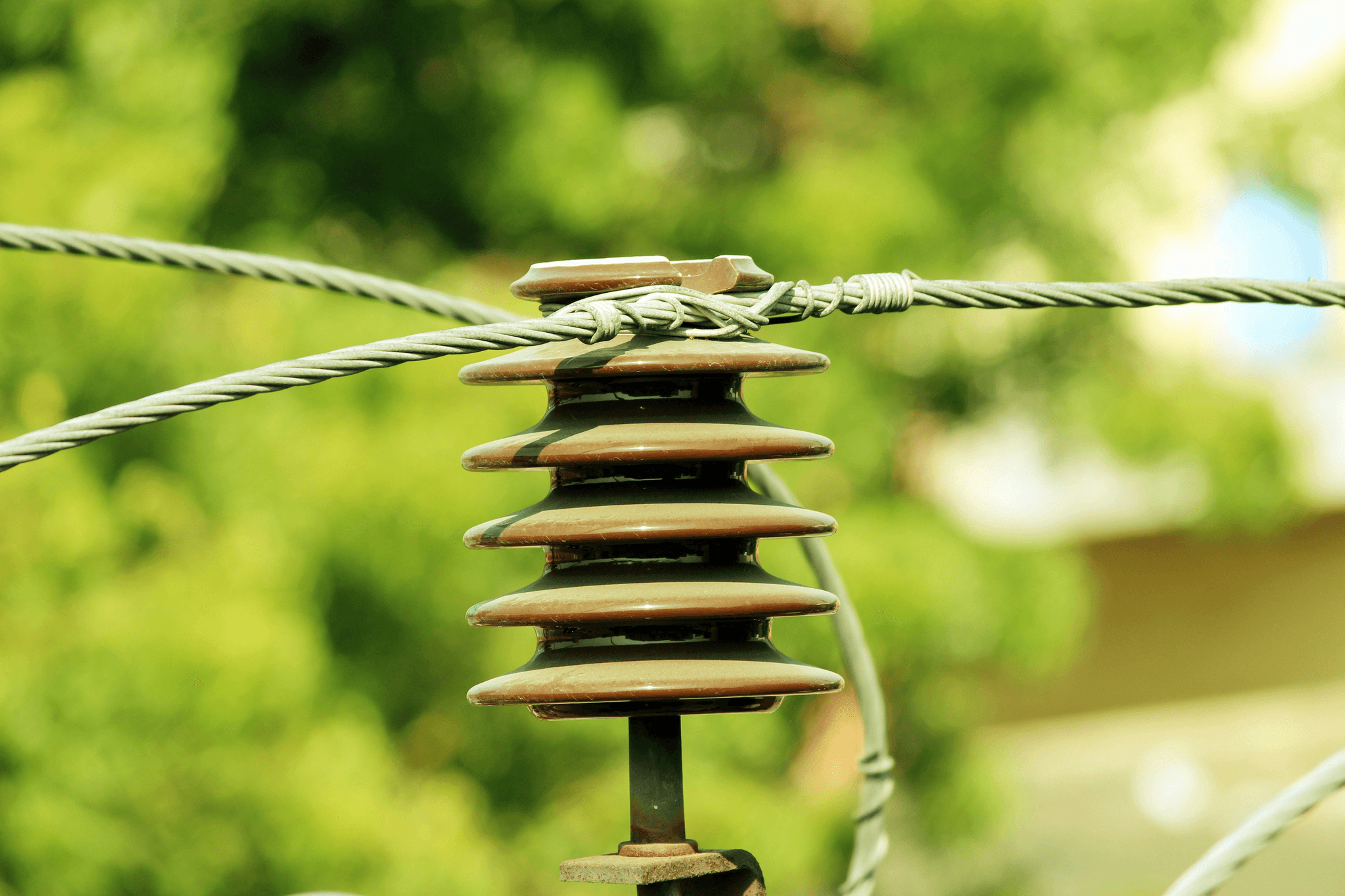
In wrapping up our exploration of transmission line insulators, it’s clear that these components play a pivotal role in the efficiency and safety of electrical transmission systems. From understanding what are transmission line insulators to recognizing the four types of insulators used in overhead transmission lines, we’ve covered a lot of ground. Additionally, knowing what are 5 good insulators can help ensure optimal performance in various applications.
Key Takeaways on Transmission Line Insulators
Transmission line insulators are crucial for maintaining the integrity of electrical systems while minimizing energy losses and ensuring safety. We learned that there are four types of insulators used in overhead transmission lines: suspension, strain, pin, and shackle insulators, each serving unique functions based on their placement and load requirements. Furthermore, understanding which insulator is used in a railway line highlights the adaptability of these components across different transportation sectors.
Importance of Insulator Quality and Safety
The quality of transmission line insulators directly impacts both operational efficiency and safety standards in electrical distribution systems. High-quality materials ensure durability against environmental factors such as weather changes and pollution—essential for long-term reliability. As we’ve seen throughout our discussion on types of insulators in transmission lines, selecting the right quality not only safeguards infrastructure but also protects human lives.
Future of Transmission Line Insulators in Energy Distribution
Looking ahead, the future of transmission line insulators seems promising with ongoing advancements in technology and materials science. Innovations such as composite materials may lead to lighter yet stronger options for insulation, enhancing performance while reducing installation costs. As energy distribution evolves with smarter grids and renewable sources, adapting insulation technology will be vital to meet new challenges effectively.

