Introduction
In the world of electrical engineering, insulators play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of power systems. Among the various types of insulators, the suspension type insulator stands out for its unique design and functionality. Understanding these components is essential for anyone involved in power transmission and distribution.
Understanding Suspension Type Insulator
A suspension type insulator is specifically designed to support overhead power lines while providing a barrier against electrical conduction. This type of insulator typically consists of multiple discs stacked together, allowing it to handle high voltage levels effectively. The flexibility in its design helps accommodate line sag and thermal expansion, making it a preferred choice for many utility companies.
Importance of Insulators in Power Systems
Insulators are vital for ensuring that electricity travels safely and efficiently from generation points to consumers. They prevent electrical leakage, which can lead to energy loss or dangerous short circuits. By using suspension type insulators, utilities can enhance system reliability while minimizing maintenance costs associated with failures caused by poor insulation.
Overview of Insulator Types
There are several types of insulators used in power systems, each serving distinct purposes based on their design and application. The most common types include suspension type insulators, disc type insulators, and strain type insulators—each offering unique advantages tailored to specific environmental conditions or load requirements. Understanding these differences is key when selecting the right insulation solution for any project.
What is a Suspension Type Insulator

Suspension type insulators are essential components in electrical power systems, specifically designed to support overhead transmission lines. Their primary function is to isolate the conductive wires from the supporting structures, ensuring safety and efficiency in electricity transmission. Understanding these insulators can help clarify their role in maintaining a stable power supply.
Definition and Functionality
A suspension type insulator is a device that suspends conductors from towers or poles while providing electrical insulation. These insulators allow for flexibility in line movement due to wind or temperature changes, which helps prevent mechanical stress on both the conductors and the support structures. Their functionality lies not only in supporting the weight of the wires but also in preventing electrical leakage to the ground.
Components of Suspension Type Insulators
Suspension type insulators consist of several key components, including porcelain or glass discs that provide insulation and strength. Each disc is connected by metal fittings, forming a chain-like structure that can be adjusted based on specific needs. The overall design ensures that even under extreme weather conditions, these insulators maintain their integrity and performance.
Comparison with Disc Type Insulators
While both suspension type insulators and disc type insulators serve similar purposes, they differ significantly in design and application. Disc type insulators are typically used for shorter spans where mechanical load is less critical, whereas suspension type insulators excel over long distances due to their ability to handle greater loads and flexibilities. This makes suspension type insulators more suitable for high-voltage transmission lines compared to their disc counterparts.
How Suspension Type Insulators Work
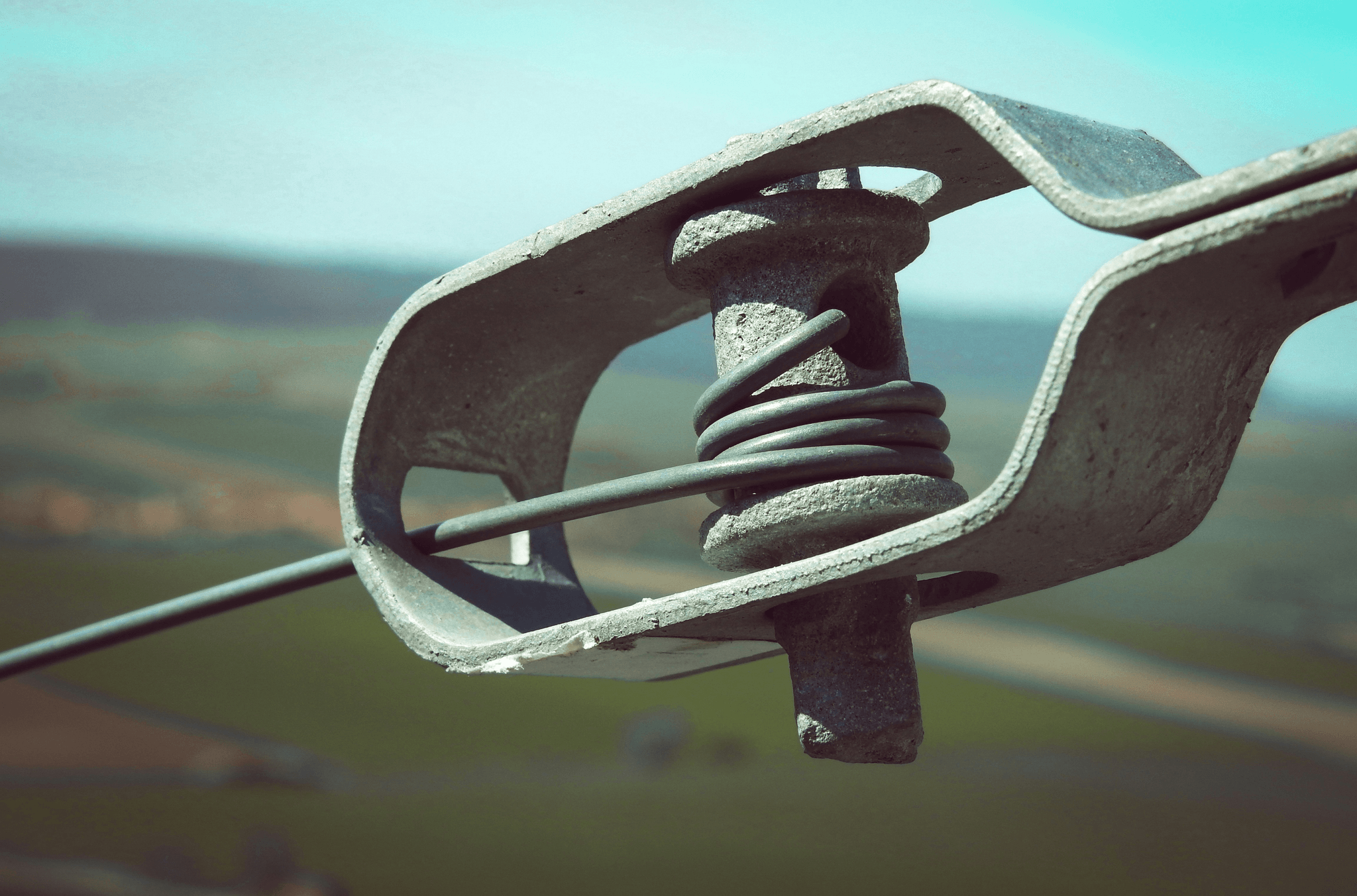
Suspension type insulators play a crucial role in electrical power transmission systems by ensuring that electrical conductors are safely supported while preventing leakage currents. Their design allows them to withstand mechanical stress and environmental factors, making them essential for maintaining the integrity of overhead lines. Understanding the electrical properties and mechanisms of these insulators is key to appreciating their function in power systems.
Electrical Properties and Mechanisms
The electrical properties of suspension type insulators are primarily determined by their material composition, geometry, and configuration. Made from high-quality materials such as porcelain or composite polymers, these insulators exhibit excellent dielectric strength, which helps prevent arcing and ensures minimal energy loss during transmission. The mechanism behind their functionality involves creating a significant air gap between the conductor and the ground or supporting structure, which effectively reduces the risk of electrical breakdown.
Moreover, suspension type insulators are designed to handle varying voltage levels while maintaining stability under load conditions. This is particularly important when compared to disc type insulators that may not provide the same level of support under extreme weather conditions or mechanical stress. By understanding these properties, engineers can select appropriate suspension type insulator sizes tailored to specific applications in power transmission.
Role in Transmission Lines
Suspension type insulators serve as critical components in overhead transmission lines where they support conductors while allowing for necessary movement due to thermal expansion or wind-induced vibrations. Their primary role is to provide mechanical strength as well as electrical insulation between energized conductors and their supporting structures, ensuring safety for both equipment and personnel working nearby. In contrast to strain type insulators, which are typically used at points where tension is applied (like dead ends), suspension type insulators excel in scenarios requiring flexibility along long spans between towers.
The arrangement of suspension type insulator sizes varies based on factors like line voltage and environmental conditions; higher voltages may require larger or more robust designs to ensure adequate insulation levels are maintained over time. This adaptability makes them indispensable for modern power grids that must accommodate increasing demand while minimizing outages caused by equipment failure or environmental impacts. Ultimately, effective use of suspension type insulators contributes significantly to reliable energy delivery across vast distances.
Suspension Type Insulator Diagram Explained
To visualize how suspension type insulators operate within a power system, a well-constructed suspension type insulator diagram can be invaluable. Such diagrams typically illustrate the arrangement of multiple insulating units connected together with metallic hardware designed for maximum stability under load conditions. Key features depicted might include the conductor's attachment points, spacing between individual units, and any additional support structures needed for optimal performance.
In examining a typical diagram, one would notice how each component works cohesively with others—showcasing how multiple suspension type insulator sizes can be stacked together depending on voltage requirements and structural design considerations. Additionally, diagrams often highlight differences from other types like disc type or strain type insulators through visual cues that indicate their respective functions within an overall system architecture. Understanding these visual representations enhances comprehension of how different configurations impact overall efficiency in transmission line operations.
Different Suspension Type Insulator Sizes
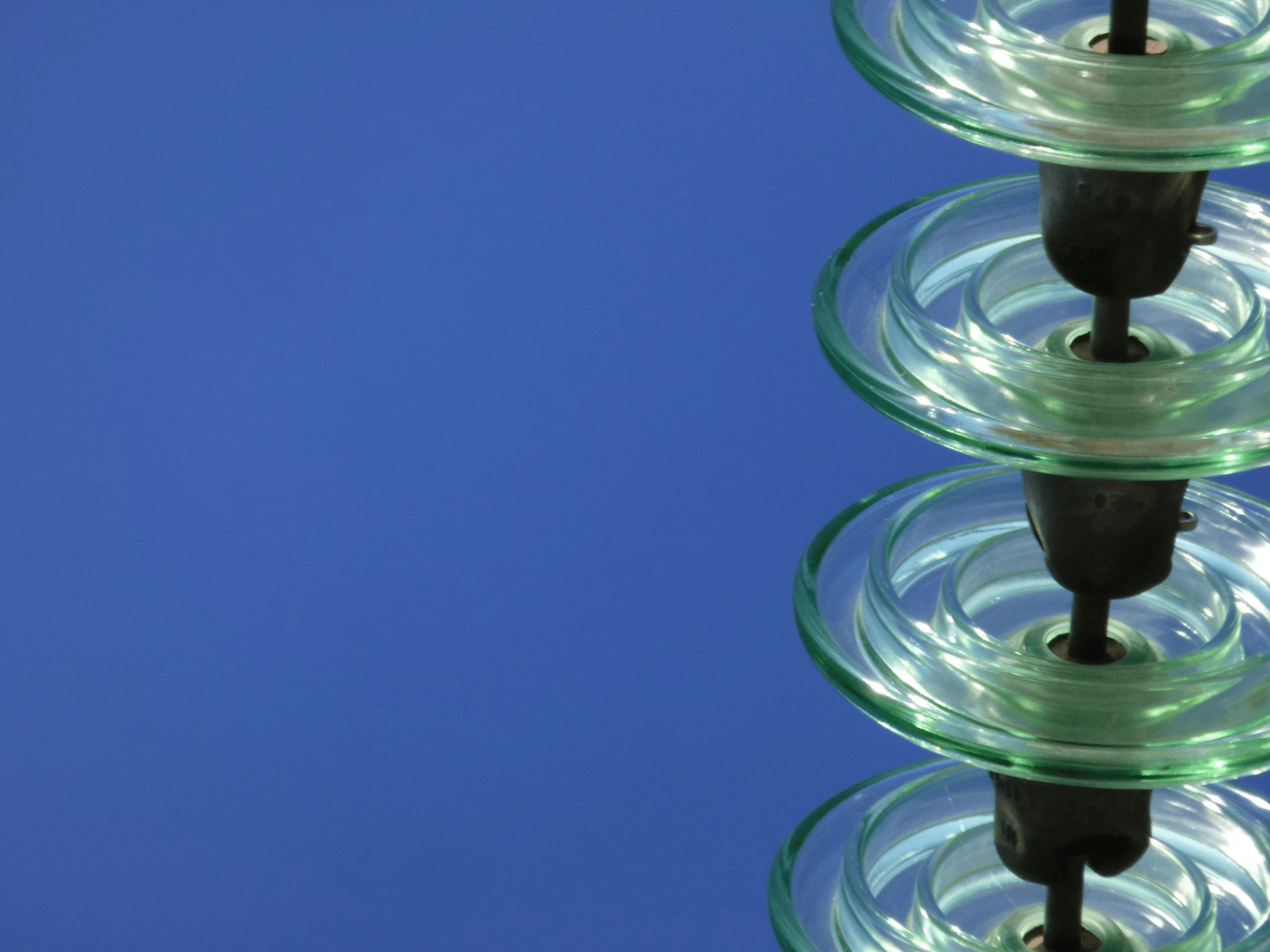

When it comes to suspension type insulators, size matters—quite literally. These insulators come in various sizes, each tailored for specific voltage levels and environmental conditions. The right suspension type insulator size ensures optimal performance in power transmission systems, preventing failures and enhancing reliability.
Common Sizes in the Industry
In the industry, you will find a range of common sizes for suspension type insulators, typically categorized by their electrical strength and mechanical load capabilities. For instance, standard sizes might include 11 kV, 33 kV, and up to 765 kV insulators designed for high-voltage transmission lines. Each size is engineered to meet specific operational demands while ensuring compatibility with other components like disc type insulators.
Factors Influencing Size Selection
Choosing the appropriate size of a suspension type insulator involves considering multiple factors such as voltage level, environmental conditions (like wind and ice loads), and installation location. Additionally, the physical distance between towers can impact the required size; longer spans often necessitate larger or more robust insulators to maintain stability and safety. Engineers must also account for regulations and standards that dictate minimum requirements based on local codes.
Manufacturer Insights on Sizing
Manufacturers provide valuable insights into selecting suspension type insulator sizes by offering data sheets that detail performance characteristics across various models. They often recommend conducting site assessments to gather information on environmental conditions before finalizing your choice of insulation system components like strain type insulators or disc type insulators. This collaboration ensures that your selected suspension type insulator not only meets but exceeds operational expectations.
Understanding Strain Type Insulators

Designed to withstand significant mechanical stress, these insulators are essential for ensuring that conductors remain securely attached while minimizing electrical leakage. Understanding their definition and purpose can help clarify their importance in contrast to other types like suspension type insulators.
Definition and Purpose
A strain type insulator is specifically engineered to support overhead power lines that experience tension due to various factors such as wind or weight from ice accumulation. Unlike suspension type insulators, which primarily hang vertically and bear the weight of the conductor, strain type insulators are oriented horizontally and are designed to manage pulling forces effectively. Their purpose is not only to hold conductors in place but also to prevent any potential sagging or breakage that could lead to power outages.
Differences Between Strain and Suspension Type Insulators
When comparing strain type insulators with suspension type insulators, one can observe distinct functional differences tied closely to their design purposes. While suspension type insulators are used mainly for vertical applications where weight support is paramount, strain type insulators excel in scenarios where tensile strength is critical—think of them as the bouncers at a nightclub for your power lines! Additionally, disc type insulators can be seen as a middle ground; they offer some tensile strength but lack the specialized design features found in dedicated strain types.
Applications of Strain Type Insulators
Strain type insulators find themselves employed across various applications within power systems, particularly in areas where high mechanical stress is expected. They are commonly used at points along transmission lines where changes in direction occur or where lines need to be anchored firmly against environmental forces. Moreover, they play an integral role in substations and towers where stability is crucial—essentially keeping everything grounded while ensuring efficient electricity flow.
Choosing the Right Insulator for Your Needs
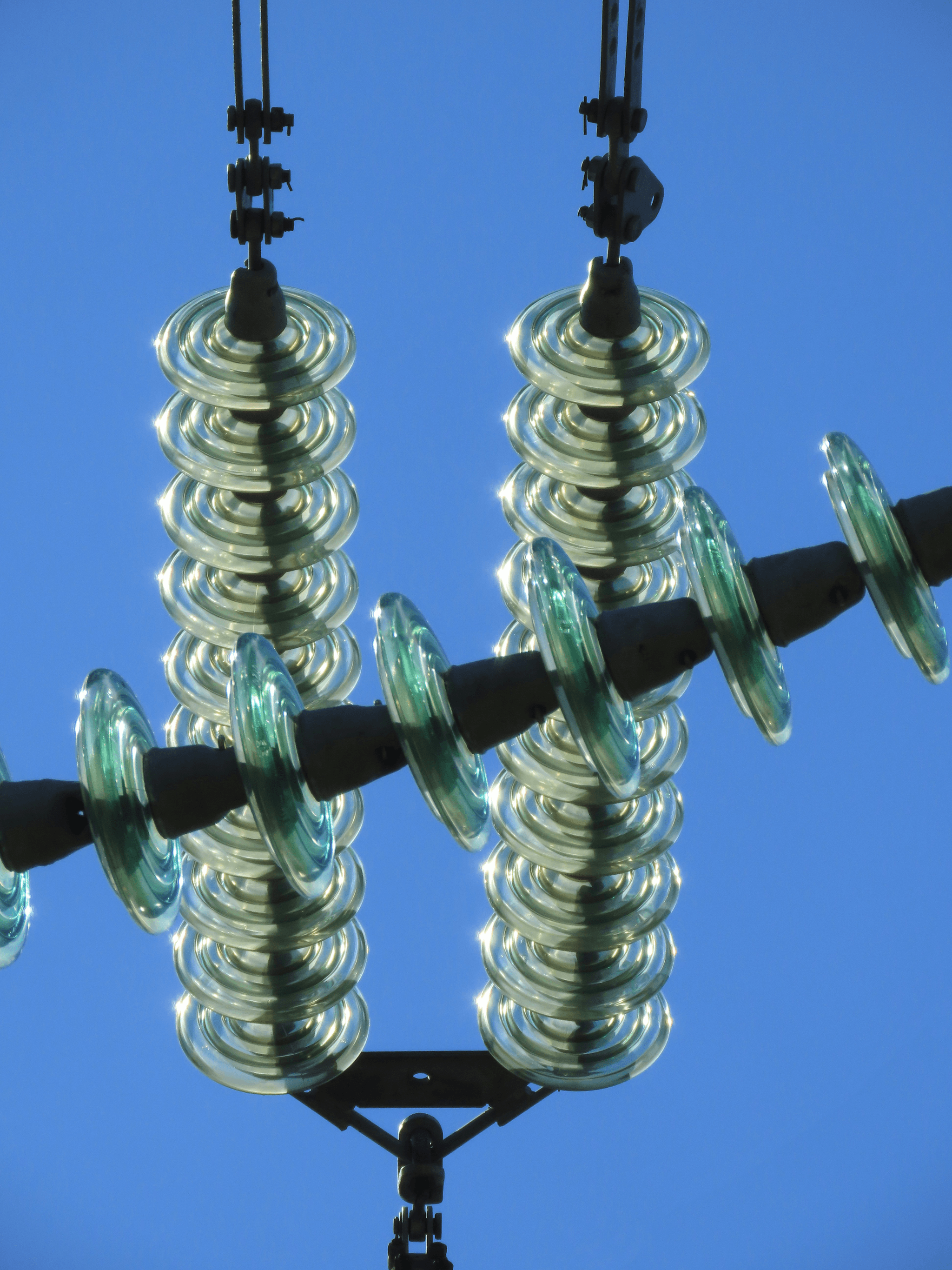
The choice often boils down to suspension type insulators and strain type insulators, each serving distinct purposes in electrical transmission. Factors such as environmental conditions, load requirements, and installation specifics will guide you toward making an informed decision.
Factors to Consider in Selection
The first step in choosing an insulator involves assessing the operational environment where it will be deployed. For instance, a suspension type insulator may be ideal for high-voltage transmission lines due to its ability to support heavy loads while maintaining electrical insulation. Additionally, consider factors like pollution levels, mechanical stress, and temperature variations; these can significantly impact the performance of both suspension type and strain type insulators.
Another essential factor is voltage rating; ensure that the selected insulator can withstand the maximum expected voltage without compromising safety or performance. The physical size of suspension type insulators also matters; you’ll find various sizes available that cater to specific applications based on load requirements and environmental conditions. Ultimately, a comprehensive assessment of these factors will lead you to the best choice for your needs.
Applications of Suspension Type Insulator vs. Strain Type Insulator
Suspension type insulators are predominantly used in overhead transmission lines where they hang from towers or poles, effectively supporting conductors while providing electrical insulation. Their design allows them to handle large spans between supports without significant sagging or mechanical stress—ideal for long-distance power transmission systems. On the other hand, strain type insulators are specifically engineered for situations where tensile strength is paramount, such as at points where cables change direction or are anchored.
In practical terms, if you're working on a project involving extensive overhead lines with minimal bends or changes in elevation, suspension type insulators are likely your best bet. Conversely, if your setup requires anchoring cables under tension—think about corners or junctions—then strain type insulators should take center stage in your selection process. Understanding these applications ensures that you choose wisely based on your project's unique demands.
Impact of Quality Insulators on System Performance
The quality of insulation materials directly influences system reliability and longevity; thus investing in high-quality suspension type and strain type insulators is non-negotiable for optimal performance. Poor-quality insulators can lead to failures such as flashovers or mechanical breakages that compromise entire power systems—an expensive mistake no one wants to make! Moreover, quality insulation contributes significantly to reduced maintenance costs over time since they tend to withstand harsh environmental conditions better than their inferior counterparts.
Additionally, superior materials enhance dielectric strength and thermal stability; this means fewer disruptions during peak loads and extreme weather events—a win-win situation for any utility provider! When evaluating options like disc-type and suspension-type designs within this context, always prioritize manufacturers known for their commitment to quality assurance standards over mere cost savings alone.
Spark Fittings and Their Role in Insulation
These fittings are designed to provide additional protection at critical points where electrical connections occur, preventing arcing and enhancing the overall safety of the installation. Understanding how spark fittings work can help you appreciate their importance in conjunction with both suspension type insulators and disc type insulators.
Overview of Spark Fittings
Spark fittings are specialized components used in overhead power lines to mitigate the risk of electrical discharge or arcing, which can damage insulators and pose safety hazards. They typically consist of conductive materials that guide electrical currents safely away from sensitive areas, thus protecting suspension type insulators from excessive stress. By integrating these fittings with strain type insulators as well as suspension types, engineers can create a more robust and resilient power transmission system.
Customization Options for Armor Rods
Armor rods are essential protective elements that work hand-in-hand with spark fittings, providing an additional layer of security for suspension type insulators. These rods can be customized in various sizes and materials to fit specific applications, ensuring they accommodate different voltage levels and environmental conditions effectively. The ability to tailor armor rods allows for optimized performance across various configurations—whether using a suspension type or strain type insulator—making them indispensable in modern power systems.
Importance of Material Matching in Armor Rods
Material matching is vital when selecting armor rods for use with any insulation system, especially when considering suspension type insulators and their unique properties. Using compatible materials helps prevent issues like corrosion or mechanical failures that could compromise the integrity of the entire system over time. Ensuring that armor rods match not only enhances the durability of spark fittings but also contributes significantly to maintaining optimal performance across all types of insulators, including disc and strain types.
Conclusion
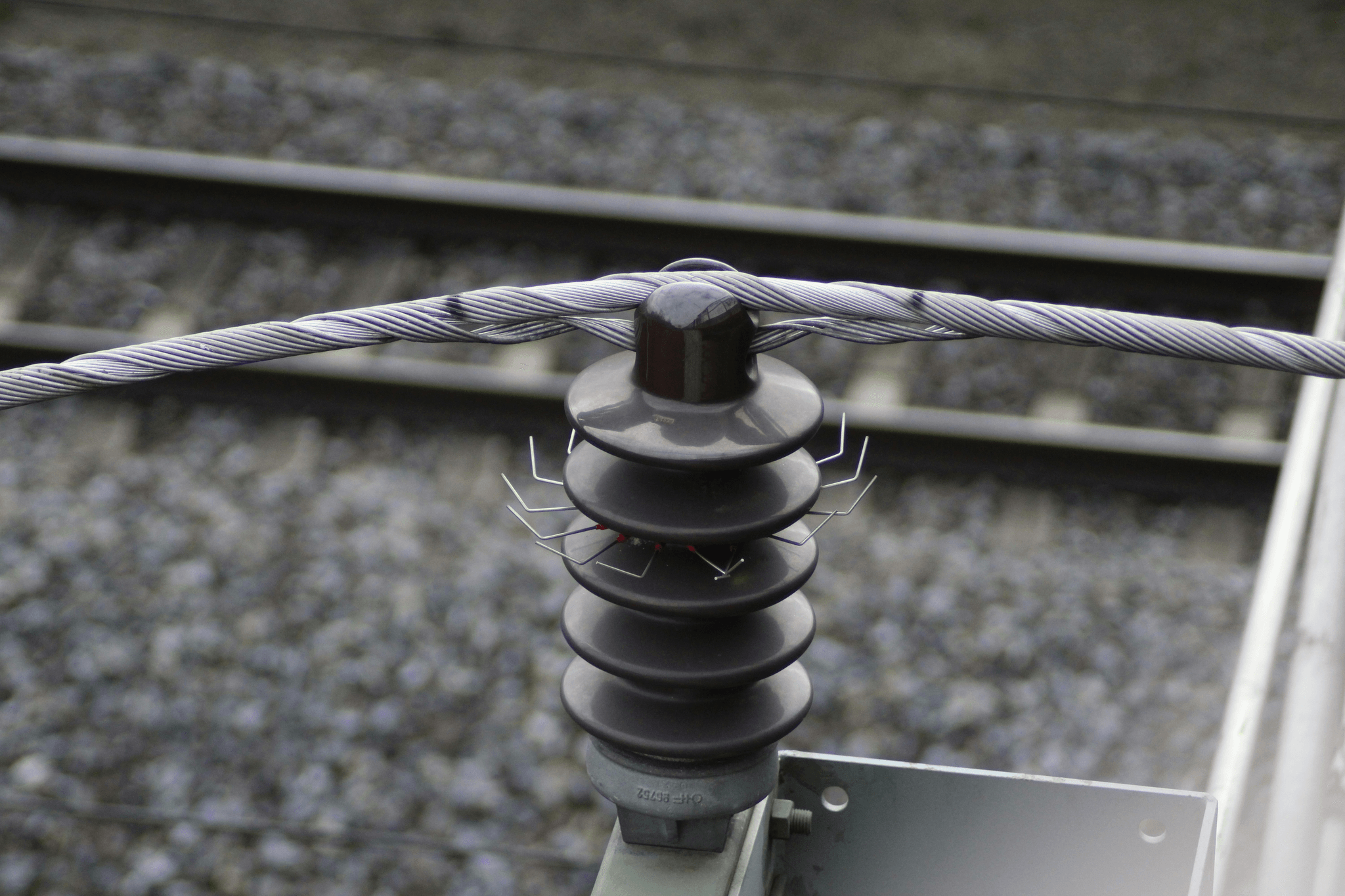
In wrapping up our exploration of suspension type insulators, it's clear that these components are vital in maintaining the integrity of power systems. Unlike disc type insulators, which serve specific purposes, suspension type insulators excel in supporting overhead lines by efficiently managing tension and electrical insulation. Their unique design and functionality make them an essential choice for various transmission applications.
Recap of Suspension Type Insulators
Suspension type insulators are designed to hang from a support structure, providing both mechanical strength and electrical insulation for high-voltage transmission lines. They consist of multiple layers or units that can be stacked to form a robust assembly capable of withstanding environmental stresses. By comparing suspension type insulators with strain type insulators, we see how each serves its unique role within the broader context of electrical infrastructure.
Key Considerations for Insulator Selection
When selecting the right insulator, several factors come into play beyond just the basic types like suspension or strain type insulators. Considerations include environmental conditions, voltage levels, and even the specific application requirements which can dictate whether a suspension type insulator or a disc type insulator is more suitable. Additionally, understanding different suspension type insulator sizes is crucial; choosing the right size ensures optimal performance and longevity in your power system.
Future Trends in Insulation Technology
Looking ahead, innovation in insulation technology promises exciting developments for suspension type insulators and their counterparts. Advances may include enhanced materials that improve durability and resistance to harsh weather conditions while reducing overall weight, making installation easier than ever before! Furthermore, integrating smart technologies could allow for real-time monitoring of insulation integrity through sensors embedded within these systems.

