Introduction
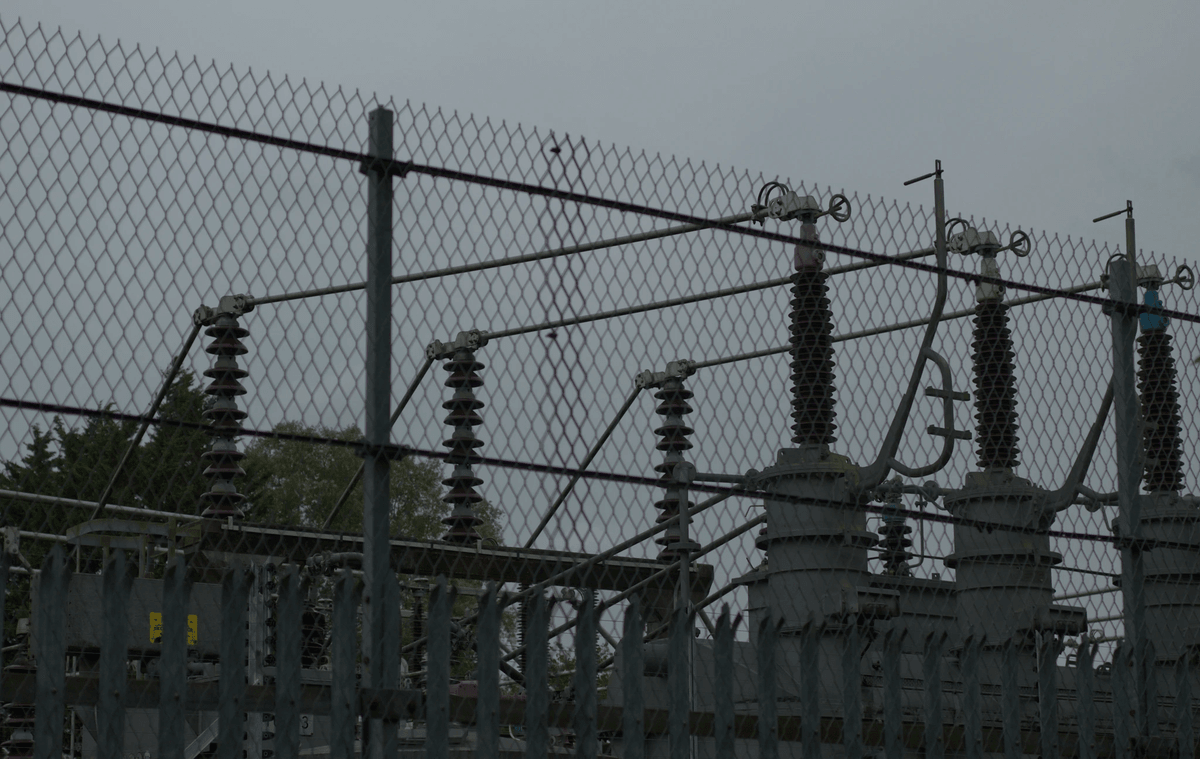
These systems are designed to mitigate the risks associated with lightning strikes, particularly for overhead power lines and electrical substations. By understanding how these protective measures work, we can appreciate their significance in maintaining the integrity of our power transmission networks.
Understanding Lightning Protection Systems
Lightning protection systems consist of various components that work together to shield structures from the devastating effects of lightning strikes. At their core, these systems often incorporate guard wire in transmission line applications to provide an additional layer of defense against surges. By directing the energy from a lightning strike safely into the ground, these systems help prevent damage to vital infrastructure like power substations and overhead power lines.
The Role of Grounding in Safety
Grounding is an essential aspect of any effective lightning protection system; it ensures that electrical faults and surges can be safely discharged into the earth. Proper grounding techniques not only protect equipment but also enhance overall safety for personnel working near electrical substations and other facilities. In combination with guard wires in transmission line setups, grounding creates a robust defense against potential hazards posed by natural phenomena like thunderstorms.
Importance of Transmission Line Protection
The protection of transmission lines is crucial for ensuring uninterrupted power supply and minimizing outages during severe weather events. Lightning strikes can cause significant disruptions if proper protective measures are not in place; therefore, investing in advanced technologies and materials is vital for maintaining system reliability. With innovations like fiberglass optic cables integrated into power line designs, utilities can enhance both safety and communication capabilities while reducing vulnerability to lightning-related incidents.
The Science Behind Lightning Strikes

When it comes to understanding the effects of lightning on power lines, it's essential to recognize that these natural phenomena can be both awe-inspiring and destructive. Lightning strikes can induce surges of electrical energy that significantly impact overhead power lines, potentially leading to outages or damage. The presence of guard wire in transmission line applications serves as a crucial first line of defense against these powerful strikes, helping to mitigate their effects on the overall electrical infrastructure.
How Lightning Affects Power Lines
Lightning has a unique way of interacting with power lines, often targeting them due to their height and conductive materials. When a bolt strikes, the immense energy can create voltage spikes that travel along the line, affecting not only the immediate vicinity but also connected systems like electrical substations. The rapid rise in voltage can lead to equipment failure or even fires if proper precautions—such as guard wire installation—aren't taken.
The consequences don't stop at mere disruptions; they can escalate into extensive damage requiring costly repairs and lengthy downtime for restoration. For instance, when lightning hits an overhead power line directly, it may cause insulation breakdowns or even physical destruction of the line itself. This is why understanding how lightning affects power lines is critical for maintaining a reliable electricity supply and ensuring safety across the grid.
The Impact on Electrical Substations
Electrical substations serve as vital nodes in the transmission network, converting high-voltage electricity for distribution while ensuring stability throughout the system. However, they are particularly vulnerable during thunderstorms when lightning strikes are most prevalent. An unexpected surge from a nearby strike can wreak havoc on transformers and other sensitive equipment within these facilities.
To combat this risk, many substations employ robust grounding techniques alongside protective measures like guard wires in transmission lines that feed into them. By creating pathways for excess energy to dissipate safely into the ground, these systems help prevent catastrophic failures that could otherwise ripple through entire regions' power supplies. Ultimately, investing in effective protection strategies at electrical substations not only safeguards equipment but also ensures continued service reliability for consumers.
Case Studies of Lightning Strikes
Exploring real-world incidents provides valuable insights into how lightning interacts with our electrical infrastructure and highlights areas where improvements are needed. One notable case occurred in a rural area where an unprotected overhead power line was struck by lightning during a severe storm; this resulted in widespread outages affecting thousands of residents for several days while repairs were made. Such events underscore the importance of implementing guard wire systems along transmission lines to lessen potential damage from similar occurrences.
Another incident involved an electrical substation that experienced multiple failures due to repeated lightning strikes over several years; each event caused significant operational disruptions and financial losses for utility companies involved. After analyzing these cases, many utilities have begun retrofitting older installations with modern protection techniques—including enhanced grounding methods and improved use of fiberglass optic cable alongside traditional conductors—to better withstand future storms effectively.
Ultimately, case studies reveal patterns that inform best practices moving forward—emphasizing proactive measures such as installing guard wires in transmission lines and reinforcing existing infrastructures against nature's unpredictable forces.
Guard Wire in Transmission Line Applications

Guard wire serves as a crucial component in the protection of overhead power lines and electrical substations. This additional layer of defense helps to mitigate the risks posed by lightning strikes and other environmental hazards, ensuring that power systems remain operational and safe. Understanding how guard wire functions can provide insights into its importance for maintaining the integrity of power transmission.
What is Guard Wire?
Guard wire is a type of conductive wire installed above or alongside overhead power lines to protect them from lightning strikes and other external threats. Typically made from steel or aluminum, this wire acts as a shield, diverting electrical surges away from critical components like fiberglass optic cables and transformers at power substations. By creating a physical barrier, guard wires help reduce the chances of direct hits on the primary conductors, thus enhancing overall system reliability.
Benefits of Using Guard Wire
The benefits of using guard wire in transmission line applications are manifold. Firstly, it significantly reduces the risk of damage caused by lightning strikes, which can lead to costly outages and repairs at electrical substations. Secondly, guard wires can also serve as grounding points during fault conditions, effectively dissipating excess energy and protecting sensitive equipment such as control systems associated with fiber optic cables embedded within power lines.
Moreover, installing guard wires enhances safety for maintenance personnel working near overhead power lines by providing an additional protective measure against unexpected electrical discharges. Overall, the integration of guard wires leads to improved operational efficiency while minimizing potential safety hazards associated with high-voltage environments.
Installation Techniques for Guard Wire
When it comes to installing guard wire in transmission line applications, several techniques ensure optimal performance and durability. The first step involves selecting appropriate materials based on environmental conditions; galvanized steel or aluminum are popular choices due to their corrosion resistance and strength.
Next comes proper placement: typically positioned above existing conductors at specific heights—often around 2-3 meters—guard wires should be securely anchored using insulators that prevent unwanted contact with live parts while allowing for efficient grounding when necessary.
Finally, regular inspections are essential post-installation to check for wear and tear or any signs of corrosion that could compromise performance over time. By adhering to these installation techniques along with best practices in maintenance, utilities can ensure that their overhead power lines remain protected against natural elements while safeguarding critical infrastructure like electrical substations.
Grounding Techniques for Overhead Power Lines
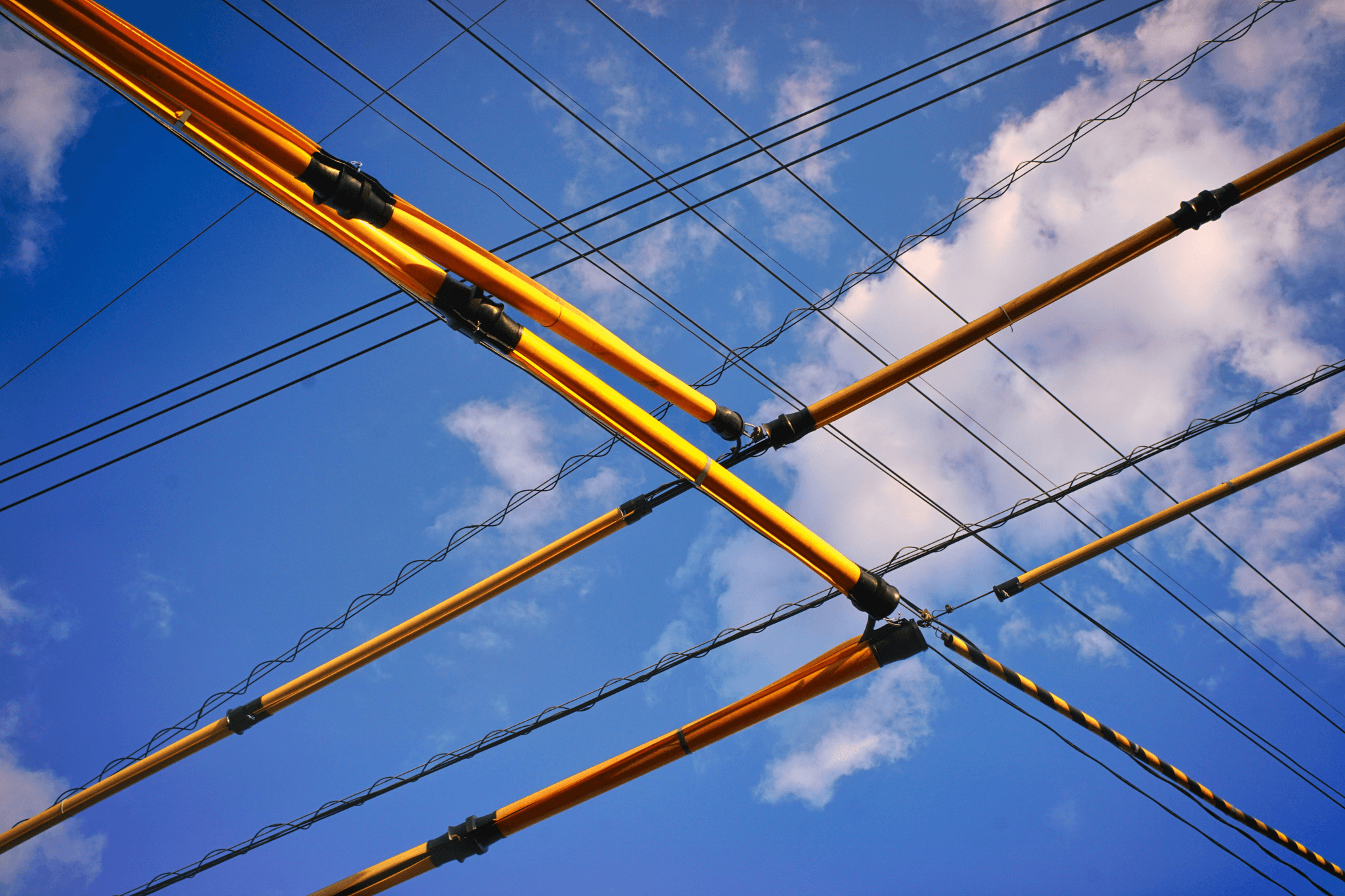
Grounding techniques for overhead power lines are crucial in ensuring safety and reliability in electrical systems. Proper grounding protects both the infrastructure and personnel from lightning strikes, surges, and other electrical faults. By implementing effective grounding methods, utilities can safeguard their power substations and maintain the integrity of the entire electrical grid.
Importance of Proper Grounding
Proper grounding is essential for minimizing the risk of electrical shock and equipment damage in overhead power lines. It provides a direct path for fault currents to flow safely into the earth, reducing potential hazards during a lightning strike or equipment failure. Moreover, effective grounding enhances the performance of guard wire in transmission line applications by ensuring that any induced voltages are effectively dissipated.
In an electrical substation context, inadequate grounding can lead to catastrophic failures or even fires due to voltage buildup during fault conditions. Thus, maintaining proper ground connections is vital not only for operational efficiency but also for overall safety within power line systems. This importance becomes even more pronounced when considering how these systems interact with sensitive components like fiberglass optic cables used in communication networks.
Best Practices for Grounding Systems
Implementing best practices in grounding systems involves several key strategies that enhance safety and reliability. First, regular inspections should be conducted to ensure that all ground connections are intact and corrosion-free; this includes checking connections at poles, transformers, and other critical points along overhead power lines. Additionally, using multiple ground rods spaced appropriately can help distribute fault currents effectively across a larger area.
Another best practice is to integrate guard wire in transmission line designs as part of a comprehensive grounding strategy; this not only protects against direct strikes but also helps reduce electromagnetic interference affecting nearby equipment like fiber optic cables. Furthermore, employing low-resistance materials such as copper or specialized alloys ensures efficient current flow during fault conditions while minimizing voltage drop across connections at substations or pole bases.
Lastly, training personnel on proper installation techniques is vital; understanding local regulations regarding grounding standards will help ensure compliance while optimizing system performance across various installations involving overhead power lines.
Grounding Materials and Their Uses
The choice of grounding materials plays a significant role in the effectiveness of overhead power line installations. Copper remains one of the most popular choices due to its excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion; it’s commonly used for ground rods and conductors connecting various components within an electrical substation or along transmission lines. However, alternatives like galvanized steel can also be employed where added durability against environmental factors is necessary.
When it comes to integrating fiberglass optic cable with existing power line infrastructure, using non-corrosive connectors ensures long-lasting performance without compromising signal integrity due to moisture exposure or oxidation over time. Additionally, specialized compounds designed for bonding different metals can improve connectivity between dissimilar materials found within modern electrical systems while maintaining robust protection against faults.
Ultimately, selecting appropriate grounding materials tailored specifically for each application—whether it’s guarding against lightning strikes with guard wire in transmission line setups or enhancing safety measures at substations—is crucial for achieving optimal results throughout an electric utility's operations.
Spark Fittings: Innovations in Protection

In the realm of electrical infrastructure, ensuring the safety and longevity of power lines is paramount. One innovative solution that has gained traction is the use of spark fittings, which serve as a critical component in protecting overhead power lines from lightning strikes and other environmental hazards. By integrating advanced materials and design techniques, spark fittings enhance the overall resilience of transmission systems.
Overview of Spark Fittings Products
Spark fittings are specialized devices designed to mitigate the risks associated with electrical surges and lightning strikes on power lines. These products include various components such as surge arresters, connectors, and protective covers that work together to safeguard electrical substations and transmission lines. The versatility of spark fittings makes them suitable for different configurations within overhead power lines, ensuring that every aspect of a transmission system is fortified against potential threats.
The implementation of spark fittings can significantly reduce maintenance costs by preventing damage to critical infrastructure. Moreover, these innovations contribute to improved reliability in energy delivery by minimizing outages caused by lightning-induced failures. As utility companies continue to adopt these technologies, the safety standards for both workers and communities surrounding power substations are greatly enhanced.
Custom Armor Rods for Transmission Lines
Custom armor rods represent a significant advancement in protecting transmission lines from mechanical stress and environmental challenges. These rods are strategically placed at critical points along overhead power lines to provide additional support against impacts from wind or falling debris while also safeguarding against lightning strikes. By using custom designs tailored to specific applications, utilities can ensure optimal protection for their unique configurations.
The integration of armor rods not only fortifies existing structures but also extends their lifespan by reducing wear over time. This proactive approach allows utility companies to maintain efficient operations without frequent replacements or repairs due to damage from external factors like storms or high winds. When combined with guard wire in transmission line applications, custom armor rods create a robust defense system that enhances overall network reliability.
The Role of Aluminum and Steel in Armor Rods
Aluminum and steel play pivotal roles in the construction of armor rods used for protecting overhead power lines. Aluminum's lightweight characteristics make it an ideal choice for reducing overall load on structures while remaining resistant to corrosion—a crucial factor given the outdoor environments these components endure. In contrast, steel offers exceptional strength properties that provide additional durability against physical impacts encountered during adverse weather conditions.
By combining aluminum's lightweight nature with steel's strength, manufacturers can produce armor rods that optimize performance without compromising safety standards in electrical substations or along transmission routes. This blend not only enhances structural integrity but also supports long-term sustainability efforts within energy sectors focused on reducing their carbon footprint through innovative materials management practices. Ultimately, selecting appropriate materials is essential when designing effective guard wire systems alongside armor rod installations for comprehensive protection strategies across power line networks.
Integrating Fiber Optic Cables with Power Lines
The integration of fiberglass optic cables with power lines represents a significant advancement in modern electrical infrastructure. These cables not only enhance communication capabilities but also provide a reliable means of monitoring and controlling power systems, especially in overhead power lines. As the demand for high-speed data transmission grows, the synergy between fiber optics and traditional power systems becomes increasingly vital.
Importance of Fiberglass Optic Cables
Fiberglass optic cables are crucial in today’s interconnected world, facilitating rapid data exchange across vast distances. Their lightweight nature makes them ideal for installation alongside overhead power lines, minimizing structural load while maximizing functionality. Moreover, these cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, ensuring that data integrity is maintained even near electrical substations where powerful currents flow.
Incorporating fiberglass optic cables into the infrastructure allows for real-time monitoring of electrical substation performance and health. This capability enhances operational efficiency by enabling utilities to respond swiftly to any anomalies or outages in the system. Thus, the importance of these cables cannot be overstated; they bridge the gap between electricity distribution and modern communication networks.
Protecting Fiber Optics in Transmission Lines
Protecting fiber optics within transmission lines is paramount to maintaining their integrity and functionality over time. The combination of guard wire in transmission line applications helps shield these delicate cables from physical damage caused by environmental factors or wildlife interference. Additionally, proper installation techniques ensure that fiberglass optic cables remain secure while still allowing for necessary movement during adverse weather conditions.
Utilizing protective conduits or sleeves around fiber optic installations can further enhance durability against harsh elements found along power line routes. These measures safeguard against potential lightning strikes as well, which can wreak havoc on both power lines and their integrated components like optical fibers. In this way, effective protection strategies contribute significantly to the longevity and reliability of both electrical and communication systems.
Future Trends in Cable Integrations
Looking ahead, the future trends in cable integrations will likely focus on enhancing resilience and efficiency within electrical infrastructures. Innovations such as smart grid technology will enable better monitoring capabilities through advanced sensors embedded within fiberglass optic cable networks alongside traditional overhead power lines. This integration will facilitate improved data analytics that can predict maintenance needs at electrical substations before failures occur.
Moreover, as renewable energy sources become more prevalent, integrating fiber optics with distributed generation systems will be crucial for managing energy flows effectively across various locations. The ongoing development of hybrid solutions combining guard wire in transmission line setups with advanced fiber optics ensures that both safety and connectivity continue to evolve hand-in-hand with technological advancements. Ultimately, these trends promise a more interconnected future where electricity distribution meets cutting-edge communication technologies seamlessly.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of power line safety, understanding the nuances of lightning protection is paramount. As we have explored, effective strategies such as implementing guard wire in transmission line systems can significantly mitigate risks associated with lightning strikes. By prioritizing these best practices, we can enhance the resilience of overhead power lines and electrical substations against nature's unpredictable fury.
Best Practices for Lightning Protection
To safeguard our infrastructure, it's crucial to adopt best practices for lightning protection that are both proactive and reactive. Utilizing guard wire in transmission line applications not only shields conductors but also provides an additional layer of security to electrical substations. Regular maintenance and inspections of grounding systems further ensure that protective measures remain effective over time.
Moreover, integrating advanced technologies like fiberglass optic cables into power lines can bolster communication networks while simultaneously protecting them from lightning-induced disruptions. These cables offer durability and flexibility, making them ideal companions for overhead power lines facing harsh weather conditions. By combining traditional protection methods with modern innovations, we can create a comprehensive approach to safeguarding our electrical infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Grounding Systems
Selecting the appropriate grounding system is a critical step in ensuring safety across all electrical installations, including power substations and overhead power lines. The right grounding techniques not only improve system reliability but also protect sensitive equipment from surges caused by lightning strikes or faults. When assessing options, it’s essential to consider factors like soil conductivity and local regulations to determine which grounding materials will be most effective.
Incorporating guard wires into grounding systems can enhance their performance by providing a direct path for lightning currents to dissipate safely into the ground. This integration ensures that both the transmission lines and surrounding structures are better protected from potential damage during severe weather events. Ultimately, investing in robust grounding solutions will pay dividends in operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs over time.
The Future of Power Line Safety
Looking ahead, the future of power line safety appears promising as innovations continue to emerge in lightning protection technology and materials science. We anticipate further advancements in guard wire applications within transmission lines that will improve their effectiveness against natural hazards while minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, incorporating smart technologies with real-time monitoring capabilities will enable utilities to respond swiftly to potential threats posed by thunderstorms or other adverse conditions.
The integration of fiberglass optic cables alongside traditional power lines also opens new avenues for enhanced communication capabilities without compromising safety standards at electrical substations or along overhead routes. This synergy between electricity and data transmission ensures that our energy infrastructure remains resilient amid growing demands for connectivity and reliability. As we embrace these changes, we must remain vigilant about maintaining best practices for lightning protection while adapting to new challenges on the horizon.

