Introduction

Overhead power lines are essential for the transmission and distribution of electricity, playing a crucial role in our daily lives. Understanding the components and types of power lines is vital for ensuring safety and efficient energy transfer. Exploring the variety of overhead power line components allows us to appreciate the complexity and importance of this infrastructure.
Understanding Overhead Power Lines
Understanding the different types of power lines, such as distribution, transmission, and subtransmission lines, is key to managing electrical systems effectively. Identifying voltage levels of power lines is crucial for safety and maintenance purposes. The classification of power lines helps in determining their specific functions and usage.
Importance of Overhead Power Line Components
The three types of power lines - overhead, underground, and submarine - each serve distinct purposes in delivering electricity to various locations. Identifying overhead power lines requires visual inspection, consulting line diagrams, and using voltage detectors to ensure safety around these high-voltage structures.
Exploring the Variety of Overhead Power Line Components
Components such as conductors, insulators, and spark fittings play critical roles in maintaining the integrity and functionality of overhead power lines. Regular inspections are essential for ensuring safety around these structures while advancements in technology continue to improve their efficiency.
Types of Power Lines

When it comes to types of power lines, there are three main categories: distribution, transmission, and subtransmission lines. Distribution lines are responsible for delivering electricity from local substations to individual customers, while transmission lines carry high-voltage electricity over long distances. Subtransmission lines act as a middleman between the two, transporting electricity from the transmission system to the distribution system.
Distribution, Transmission, and Subtransmission Lines
Distribution lines are typically found in residential and commercial areas, running along streets and through neighborhoods. They operate at lower voltages compared to transmission lines, which can be identified by their taller towers and larger insulators. Subtransmission lines bridge the gap between the two by carrying medium-voltage electricity from substations to distribution systems.
How to Identify Voltage of Power Lines
Identifying the voltage of power lines is crucial for safety reasons. One way to do this is by observing the size and height of the towers or poles supporting the power lines. Taller structures often indicate higher voltage transmission lines, while smaller poles may signify distribution or subtransmission lines. Additionally, color-coded markers on the poles can also provide information about the voltage level.
Classifications of Power Lines
Power lines are classified based on their voltage levels and functions within the electrical grid, with different types serving specific purposes in the transmission and distribution of electricity. Understanding these classifications is crucial for utility workers and engineers to effectively manage and maintain the power grid. By categorizing power lines, it becomes easier to identify potential issues, plan for upgrades, and ensure that the right safety measures are in place for each type of line.
Overhead Power Line Components
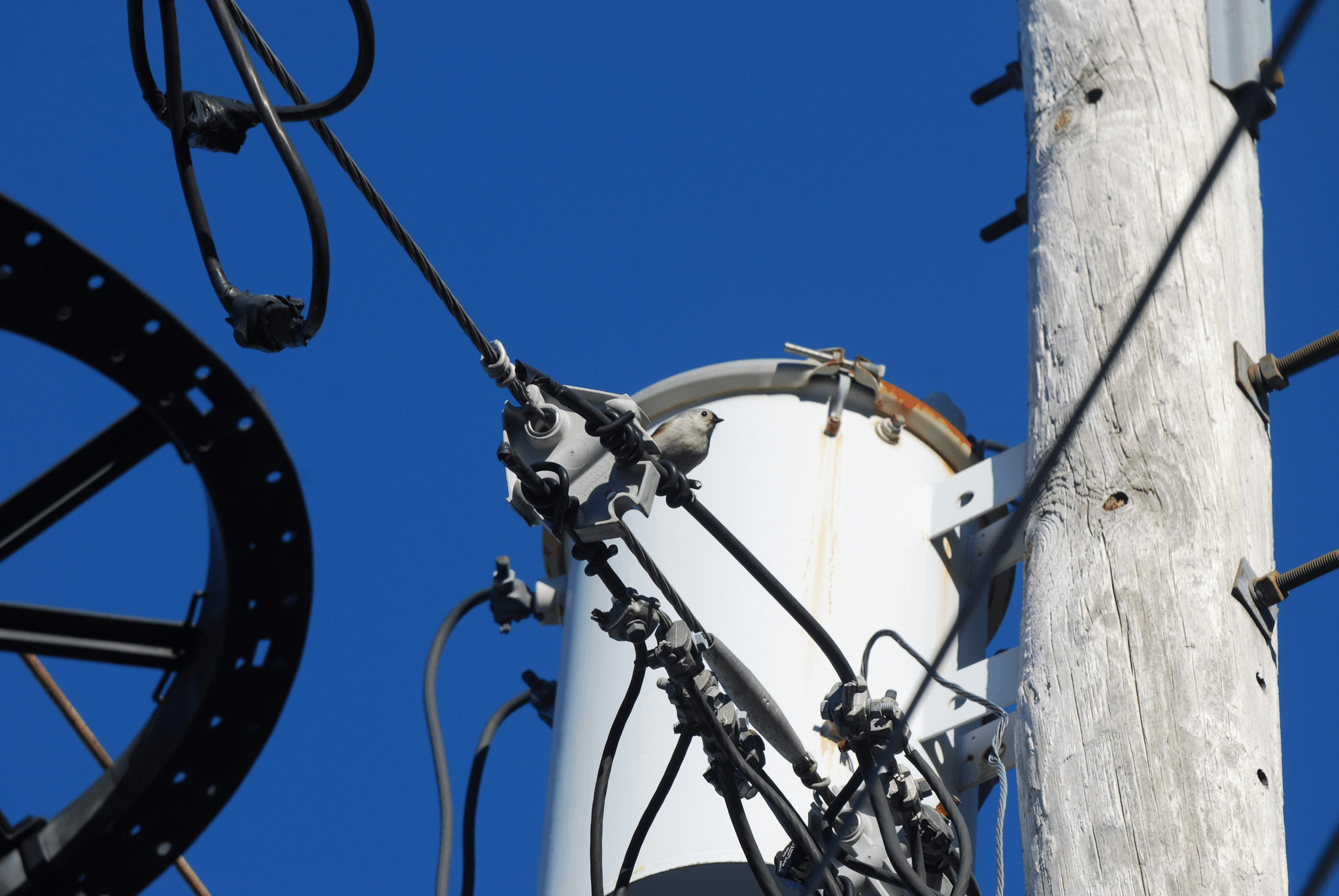
Conductors
Conductors are essential components of overhead power lines, carrying the electrical current from the power source to the end users. They are typically made of aluminum or copper, due to their excellent conductivity properties. The size and type of conductor used depend on the voltage and current capacity required for a specific power line.
Insulators
Insulators play a crucial role in overhead power lines by preventing the flow of electricity to the ground. They are typically made of porcelain or glass and are designed to withstand high voltage levels without allowing current leakage. Insulators are installed at regular intervals along the length of the conductor to support it and maintain electrical isolation.
Spark Fittings
Spark Fittings, as provided by Spark Fittings, play a vital role in ensuring the safety and reliability of overhead power lines. These fittings include equipment for preformed armor rods, tension clamps, and cable accessories for ADSS and OPGW systems, which are essential for efficient transmission and distribution of electricity.
By understanding the various components that make up overhead power lines, such as conductors, insulators, and spark fittings, it becomes easier to identify their functions within the system. This knowledge is crucial for ensuring proper maintenance and safety measures around these vital infrastructure elements.
Remember to always exercise caution when working near power lines or attempting to identify them. Proper training on how to identify voltage levels using appropriate tools is essential for avoiding accidents or electrical hazards. Additionally, regular inspections and adherence to safety guidelines can help mitigate potential risks associated with overhead power lines.
Identifying Power Lines

When it comes to identifying power lines, there are several methods that can be utilized. Visual inspection is a common way to identify power lines, as it allows for a physical assessment of the lines and their components. Consulting line diagrams is another effective method, as these diagrams provide detailed information about the layout and structure of the power lines. Using voltage detectors is also crucial for identifying power lines, as they help in determining the voltage levels of the lines, ensuring safety protocols are followed.
Visual Inspection
Visual inspection involves physically examining the power lines and their components to identify any potential issues or hazards. This method allows for an up-close assessment of the condition of the lines, such as signs of wear and tear or damage to components like insulators or conductors. It also provides an opportunity to spot any vegetation encroachment or other obstacles that may pose a risk to the power lines.
After conducting a visual inspection, the next step in ensuring the safety and reliability of power lines is consulting line diagrams. These diagrams provide detailed information about the layout and configuration of the power lines, including the location of poles, conductors, and other components. By cross-referencing the information obtained from visual inspection with the details in the line diagrams, technicians can gain a comprehensive understanding of any potential issues or hazards that may need to be addressed. This method helps to ensure that no aspect of the power line system is overlooked in the assessment process.
Consulting Line Diagrams
Line diagrams are essential tools for identifying power lines, as they provide detailed visual representations of the layout and structure of the lines. These diagrams include information about the types of power lines, their classifications, and how they are interconnected within a network. By consulting these diagrams, utility workers can gain valuable insights into how different components are arranged and connected within the system.
Using Voltage Detectors
Voltage detectors play a crucial role in identifying power lines by determining the voltage levels present in specific areas. This is essential for ensuring that workers are aware of potential electrical hazards when working near power lines. By using voltage detectors, utility workers can accurately assess whether a line is energized and take necessary precautions to avoid accidents or injuries.
Voltage detectors are also instrumental in preventing accidental contact with live power lines, which can result in serious injuries or fatalities. By using these tools, utility workers can verify the absence of voltage before starting maintenance or repair work on power lines, ensuring their safety. This proactive approach helps minimize the risk of electrical accidents and promotes a culture of safety within the utility industry.
Three Types of Power Lines

When it comes to types of power lines, there are three main categories: overhead, underground, and submarine lines. Overhead power lines are the most common and are easily identifiable by the tall poles or towers that support them. Underground power lines are buried beneath the ground, making them less visible but also less susceptible to weather-related damage. Submarine power lines run along the ocean floor and are commonly used to connect islands to mainland power grids.
Overhead, Underground, and Submarine Lines
Overhead power lines are typically seen running alongside roads or through rural areas on large transmission towers. Underground power lines can be found in urban areas where aesthetics and safety are a concern, as they eliminate the need for unsightly poles and reduce the risk of accidental contact. Submarine power lines connect offshore wind farms or islands to mainland electrical grids.
Overhead power lines are a common sight in many areas, but they can also pose a risk to birds, especially large raptors like eagles and hawks. To mitigate this risk, some power companies are exploring ways to make power lines more visible to birds, such as using UV-reflective or patterned materials. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop new technologies that can detect when a bird is approaching a power line and activate deterrent devices to prevent collisions.
Identifying Overhead Power Lines
Identifying overhead power lines is crucial for safety reasons, as accidental contact with these high-voltage wires can be extremely dangerous. Overhead power lines can be identified by their height above ground level, the presence of insulators on the poles or towers that support them, and warning signs indicating their presence. It's important to always assume that overhead wires are energized and maintain a safe distance when working near them.
When working near overhead power lines, it's important to be aware of any equipment or machinery that could potentially come into contact with the wires. This includes cranes, ladders, and even long-handled tools. Always survey the area before starting work to ensure that there are no potential hazards that could lead to accidental contact with the power lines. Additionally, it's crucial to communicate with other workers on the site about the location of overhead wires and establish clear safety protocols to prevent any accidents.
Conclusion

When working around power lines, safety precautions are essential to prevent accidents and injuries. Regular inspections of overhead power line components, such as conductors and insulators, are crucial to ensure the system's integrity and reliability. Advancements in power line technology have led to improved safety features and efficiency in the transmission and distribution of electricity.
Safety Precautions around Power Lines
It is vital to maintain a safe distance from power lines at all times to avoid the risk of electric shock or electrocution. Workers should always use insulated tools and equipment when working near overhead power lines to minimize the potential for accidents. Proper training on identifying different types of power lines is also essential for anyone working in proximity to them.
In addition to using insulated tools and equipment, it is crucial for workers to be aware of their surroundings and avoid any contact with power lines. This includes being mindful of any machinery or equipment that may come into close proximity with overhead power lines. Regular inspections of the work area should also be conducted to ensure that there are no potential hazards or obstructions that could pose a risk near power lines.
Importance of Regular Inspections
Regular inspections of overhead power line components help identify any signs of wear, damage, or corrosion that could compromise their performance. By conducting routine maintenance checks, potential hazards can be addressed promptly, ensuring the safety and reliability of the entire system. This proactive approach also minimizes the risk of unexpected outages and disruptions.
Regular inspections of overhead power line components are essential for ensuring the continued functionality and safety of the entire system. By identifying signs of wear, damage, or corrosion early on, maintenance teams can address potential hazards promptly, preventing any major disruptions or outages. This proactive approach not only saves time and resources but also helps maintain a reliable power supply for communities and businesses.
Advancements in Power Line Technology
With advancements in power line technology, there has been a focus on developing more durable materials for components such as insulators and conductors. These improvements contribute to enhanced performance and longevity of overhead power lines, ultimately leading to a more reliable electrical infrastructure. Additionally, the integration of smart grid technology allows for real-time monitoring and control of power flow, reducing the risk of outages and improving response times to potential issues. Furthermore, the use of composite materials in power line construction not only increases resilience to harsh weather conditions but also reduces maintenance costs over time.

