Introduction
In the world of power lines, insulators play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient transmission of electricity. These components are essential in preventing electrical leakage and maintaining the integrity of high voltage systems. Among the various types of power line insulators, pin insulators and post insulators stand out due to their unique designs and applications.
Understanding Insulators in Power Lines
Insulators are non-conductive materials that support and separate electrical conductors from other structures, preventing unintended current flow. They are vital in power line construction, especially when dealing with high voltage situations where safety is paramount. The choice of insulator affects not only performance but also the overall cost associated with insulator construction, making it imperative for insulator companies to select suitable options.
Why Pin and Post Insulators Matter
Pin and post insulators serve distinct purposes within power line infrastructure, impacting both functionality and cost-efficiency. Pin insulators are often used for lower voltage applications while post insulators cater to higher voltage demands, each affecting the price of insulator differently based on material and design complexity. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone involved in selecting or purchasing power line insulators.
The Role of Spark Fittings in Insulator Construction
Spark fittings play a significant role in enhancing the performance of both pin and post insulators by providing additional protection against electrical discharges. These fittings ensure that even under extreme conditions, such as storms or heavy winds, the integrity of high voltage systems remains intact. By integrating spark fittings into their designs, manufacturers can improve safety standards while also addressing concerns related to the price of insulator products.
What is a Pin Insulator?
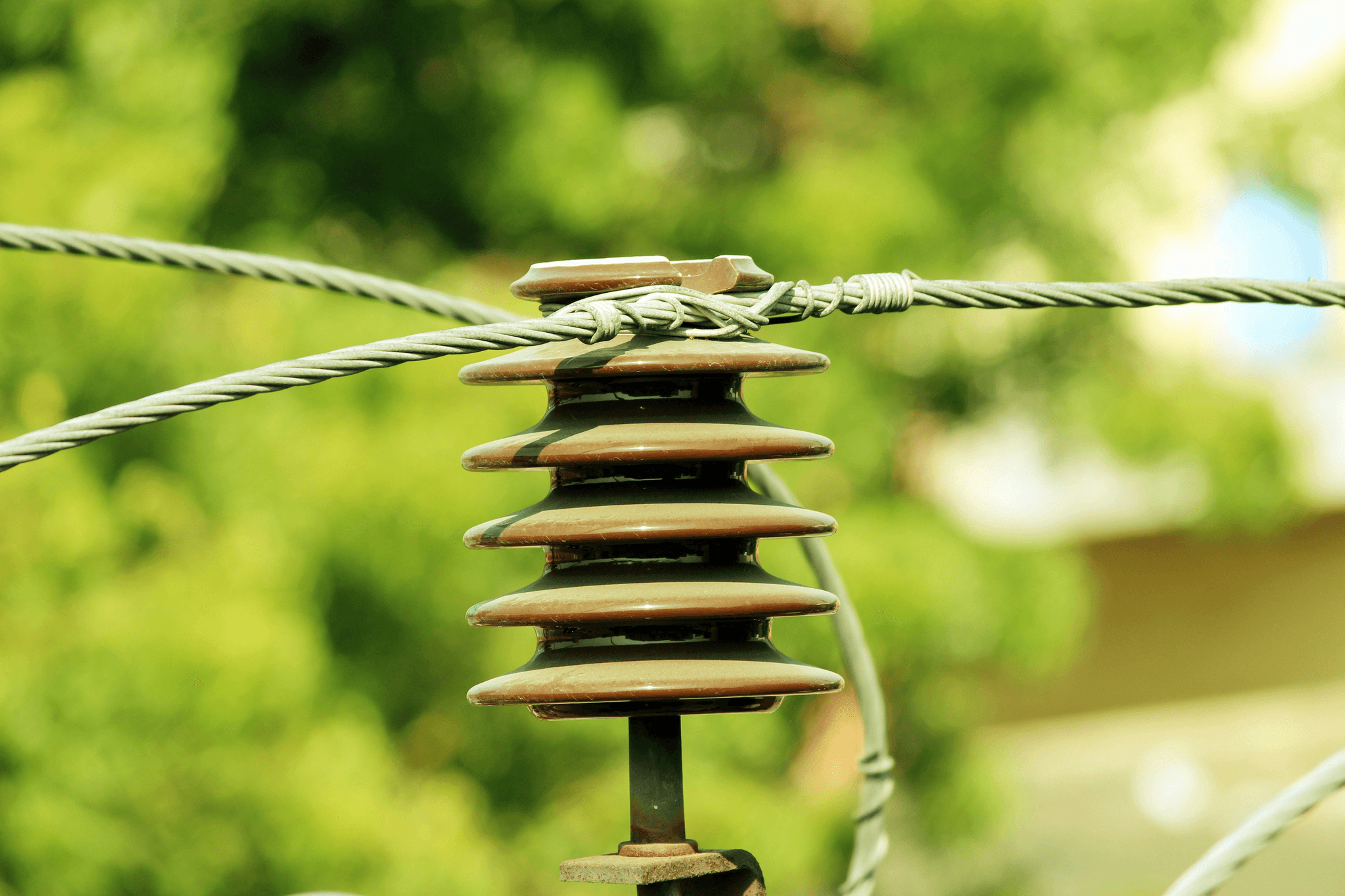
Pin insulators are crucial components in the realm of power line construction, serving as the unsung heroes that ensure electrical safety and efficiency. These high voltage insulators are designed to secure overhead power lines to utility poles, preventing electrical current from escaping and maintaining system integrity. Understanding their definition and usage is essential for anyone involved in the insulator industry or looking to purchase power line insulators.
Definition and Usage
A pin insulator is a type of electrical insulator that attaches directly to a pole via a pin, which allows it to support overhead conductors while providing insulation from the pole itself. Typically made of materials like porcelain or glass, these insulators prevent electricity from leaking into the environment, thus safeguarding both infrastructure and individuals. The versatility of pin insulators makes them widely used in various applications, particularly for low- to medium-voltage distribution systems.
Advantages of Pin Insulators
One significant advantage of pin insulators is their cost-effectiveness; they often present lower prices compared to other types of high voltage insulators due to simpler designs and materials used in their construction. Additionally, their robust structure offers excellent durability against environmental factors such as wind, rain, and ice accumulation—making them reliable even under challenging conditions. Furthermore, pin insulators are relatively easy to install, which can significantly reduce labor costs for an insulator company during construction projects.
Common Applications in the Field
Pin insulators find common application in numerous settings within the electrical industry. They are predominantly utilized in distribution lines where lower voltages are present but still require reliable insulation solutions for safety and performance. Moreover, these versatile components can also be found in street lighting systems and other urban infrastructure projects where effective power transmission is essential without compromising public safety.
What is a Post Insulator?
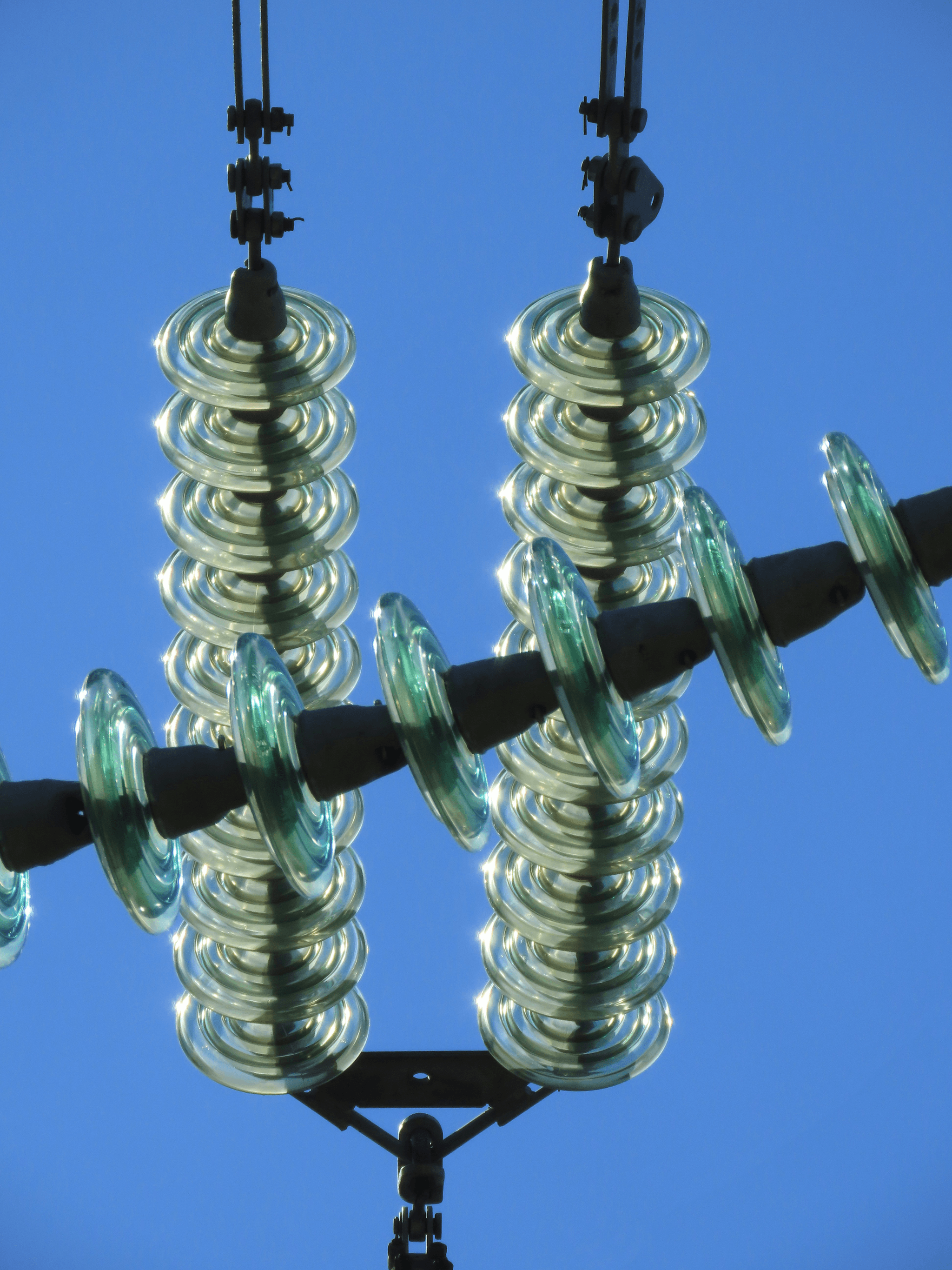
Post insulators are critical components in the world of power line infrastructure, designed to support and insulate electrical conductors. Unlike pin insulators, which are primarily mounted on poles, post insulators stand tall and robust, often used in substations and at the bases of transmission towers. Their unique design allows them to handle high voltage applications effectively while providing necessary electrical isolation.
Definition and Usage
A post insulator is a type of high voltage insulator typically constructed from ceramic or polymer materials that support overhead power lines by holding conductors in place while preventing electrical leakage to the ground. These insulators can be found in various configurations, including vertical or horizontal arrangements, depending on their application requirements. Their primary usage revolves around ensuring that power line conductors remain securely positioned and insulated from surrounding structures, making them essential for safe electricity distribution.
Benefits of Post Insulators
One of the key benefits of post insulators is their ability to withstand extreme weather conditions without compromising performance, which is crucial for ensuring reliability in power line operations. They also provide superior mechanical strength compared to pin insulators, allowing them to support heavier loads and withstand higher wind speeds. Additionally, post insulators typically have a lower overall cost when considering long-term maintenance needs due to their durable construction materials.
Typical Applications and Features
Post insulators are commonly used in substations where they facilitate connections between different components of the electrical grid while maintaining safety standards for high voltage systems. They can also be found at the base of transmission towers where they play a pivotal role in supporting heavy conductor cables over vast distances. Features such as pollution-resistant surfaces and customizable designs allow these insulators to meet specific operational demands while keeping costs manageable for an insulator company looking to optimize its product offerings.
Key Differences Between Pin and Post Insulators
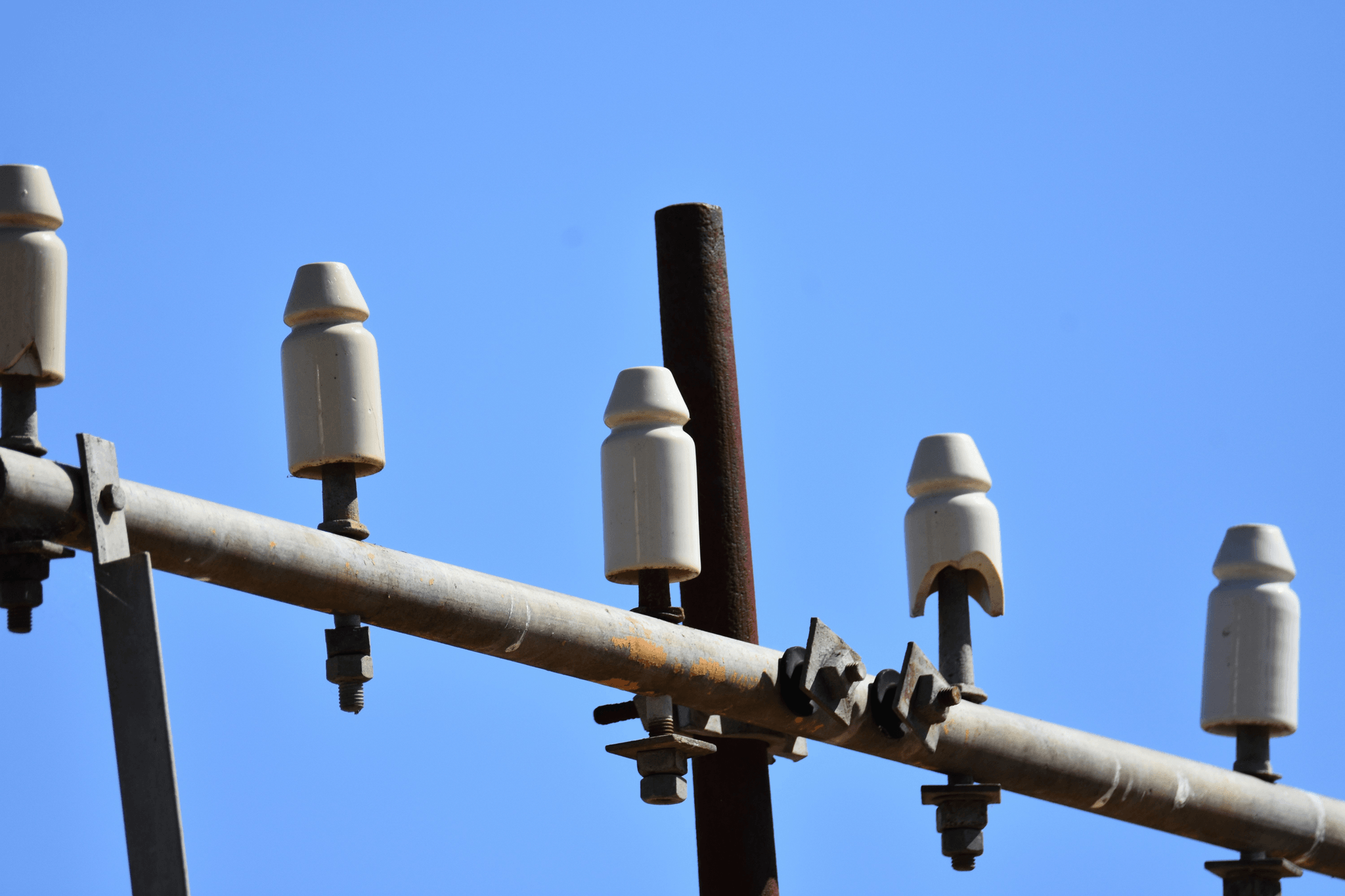
When it comes to power line insulators, pin and post insulators serve distinct roles, each with unique characteristics that impact their performance and application. Understanding these differences can assist utility companies in making informed decisions regarding insulator construction for high voltage situations. From design variations to installation challenges, the nuances between pin and post insulators are crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical distribution.
Design and Structure Variations
Pin insulators typically feature a simpler design, consisting of a single piece mounted on a pin or cross-arm, making them easier to install on existing structures. In contrast, post insulators boast a more complex structure that often includes multiple components designed to support higher loads and provide better insulation properties. This structural variation not only influences the price of insulator options but also affects their suitability for specific applications within an insulator company’s product lineup.
The design differences also extend to aesthetics; while pin insulators are generally compact and straightforward, post insulators can be larger with various shapes tailored for specific voltage requirements. This distinction is essential when considering high voltage insulators where surface leakage distance becomes critical. Ultimately, the choice between pin or post designs depends on the operational needs of the power lines they will serve.
Performance in High Voltage Situations
Performance under high voltage conditions is another area where pin and post insulators diverge significantly. Pin insulators are typically effective at lower voltages but may struggle in extreme conditions due to their limited surface area for electrical insulation. Conversely, post insulators are specifically engineered to handle higher voltages with greater efficiency due to their larger size and enhanced dielectric properties.
The ability of an insulator company to provide solutions that meet these performance standards is vital when selecting products for demanding environments. When evaluating options based on the price of an insulator versus its performance capabilities, it’s crucial to consider how well each type will hold up under potential electrical stresses during operation. Therefore, understanding these performance metrics can help utilities avoid costly failures in their infrastructure.
Installation Considerations and Challenges
Installation plays a pivotal role in determining which type of power line insulation is most appropriate for a given project. Pin insulators generally offer easier installation processes since they can be retrofitted onto existing structures without extensive modifications or additional support systems required by heavier post types. However, this simplicity comes at a cost—pin installations may require more frequent maintenance compared to robust post installations designed for longevity.
On the flip side, while post insulator installation might demand more resources upfront due to their weight and complexity, they often lead to reduced maintenance costs over time because of their durability in high voltage environments. Insulator companies must weigh these factors carefully when advising clients on which option best suits their needs while keeping budget constraints like the price of an insulator in mind. In conclusion, understanding installation challenges can significantly influence project timelines as well as overall effectiveness in delivering reliable power line insulation solutions.
Challenges Faced by Insulator Companies

Insulator companies face a myriad of challenges that can significantly impact their operations and profitability. From fluctuating insulator prices to the complexities of supply chain management, these factors require strategic planning and adaptability. Additionally, ensuring quality standards and safety in the production of power line insulators is paramount, especially when dealing with high voltage insulators.
Pricing Strategies for Insulators
Determining the price of insulator products can be a tricky balancing act for manufacturers. Pin insulators, for instance, must be competitively priced while still reflecting the quality and durability that customers expect. Fluctuations in raw material costs can lead to unpredictable changes in pricing strategies, making it essential for an insulator company to monitor market trends closely.
To maintain a competitive edge, many companies are exploring innovative pricing models or value-added services that justify higher prices for their pin insulators. By offering warranties or enhanced customer support, they can create more value around their products without simply slashing prices. Ultimately, a well-crafted pricing strategy can help an insulator company thrive even amidst market volatility.
Managing Supply Chain for Insulator Construction
The supply chain for insulator construction is another area fraught with challenges that require careful navigation. Sourcing high-quality materials like aluminum and steel is critical to producing reliable power line insulators; however, global supply chain disruptions can complicate this process. An efficient supply chain not only ensures timely delivery but also helps keep the price of insulators competitive.
Moreover, maintaining relationships with suppliers is crucial so that an insulator company can secure consistent material availability while managing costs effectively. This often involves negotiating contracts that account for price fluctuations and potential shortages in raw materials essential for manufacturing pin and post insulators alike. A robust supply chain strategy will ultimately enhance resilience against unforeseen disruptions.
Ensuring Quality Standards and Safety
Quality standards are non-negotiable when it comes to high voltage insulators; any compromise could result in catastrophic failures or unsafe conditions on power lines. Insulator companies must adhere to stringent industry regulations while also implementing their own internal quality control processes to ensure every pin insulator meets safety benchmarks before reaching consumers' hands. This commitment not only protects end-users but also safeguards the company's reputation in a competitive marketplace.
In addition to regulatory compliance, ongoing testing and innovation play critical roles in enhancing product performance over time as technologies evolve within the industry. Companies must invest resources into research and development initiatives focused on improving existing designs or creating new solutions tailored to specific applications within power line infrastructure. Ultimately, prioritizing quality standards ensures long-term success while fostering trust among clients who rely on these vital components for safe electrical transmission.
The Role of Material Choices in Insulator Performance
When it comes to power line insulators, the materials used in their construction can significantly influence their performance and longevity. Insulator companies often weigh the pros and cons of various materials, particularly aluminum and steel, to determine which will best meet the demands of high voltage applications. The right material choice not only affects durability but also impacts the overall insulator price, making it a crucial consideration for both manufacturers and consumers.
Impact of Aluminum and Steel in Insulators
Aluminum is a popular choice for pin insulators due to its lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion. This makes aluminum ideal for various environmental conditions, ensuring that power line insulators maintain their integrity over time. On the other hand, steel offers strength and durability; however, its susceptibility to rust can be a drawback unless adequately treated or coated.
The decision between aluminum and steel often hinges on specific application needs—such as load-bearing capacity or environmental exposure—ultimately affecting the price of insulator products. Insulator companies must evaluate these factors meticulously when designing high voltage insulators to ensure they meet safety standards while remaining cost-effective. By selecting the appropriate material based on these criteria, they can optimize performance without compromising on quality.
Importance of Armor Rod Material Matching
Armor rods play an essential role in enhancing the reliability of pin insulators by providing additional protection against mechanical stress and environmental factors. Matching armor rod materials with those used in the main body of an insulator is critical for ensuring compatibility and maximizing performance under high voltage conditions. A mismatch could lead to premature failure or decreased efficiency, ultimately impacting safety.
Insulator construction that incorporates well-matched materials not only prolongs service life but also reduces maintenance costs over time—a significant benefit given fluctuating insulator prices in today’s market. Companies that prioritize this aspect are better positioned to deliver dependable solutions that meet industry standards while addressing customer concerns regarding long-term investments in power line infrastructure. Therefore, careful selection during manufacturing processes becomes imperative.
Spark Fittings’ Customized Solutions
Spark Fittings has carved out a niche by offering customized solutions tailored specifically for unique operational requirements within power line systems. Their expertise allows them to provide specialized designs that consider both material choices and application contexts—ensuring optimal performance from pin insulators under varying conditions. This level of customization helps clients navigate challenges related to high voltage installations more effectively.
Moreover, Spark Fittings understands that no two projects are alike; hence they focus on delivering solutions that cater directly to client specifications while keeping an eye on cost-effectiveness amidst fluctuating prices in the industry. Their commitment extends beyond just providing products; it includes supporting clients through every step—from design considerations related to material choices all the way through installation challenges faced with different types of power line insulators. Ultimately, this approach fosters stronger partnerships between manufacturers and users alike.
Conclusion
In the world of power line insulators, understanding the distinctions between pin and post insulators is crucial for engineers and utility companies alike. Pin insulators, with their straightforward design and ease of installation, are often favored for lower voltage applications. Conversely, post insulators shine in high voltage scenarios where their robust construction can withstand greater electrical stress. Each type serves its purpose in ensuring reliable electricity transmission while maintaining safety standards.
Summary of Pin vs. Post Insulators
Pin insulators are typically used in overhead power lines where they attach directly to the pole or tower, providing a simple yet effective solution for insulation needs. On the other hand, post insulators are designed to handle higher voltages and are often utilized in substations or critical junctions within power distribution systems. While both types play pivotal roles in insulator construction, their specific applications cater to different requirements based on voltage levels and environmental conditions.
Insights into Insulator Pricing and Quality
The pricing strategies must balance affordability with quality assurance since subpar materials can lead to failures in high voltage applications, ultimately costing more in repairs or replacements down the line. As industries evolve toward more sustainable practices, we may see shifts in pricing structures influenced by innovations that enhance both performance and longevity.
The Future of Power Line Insulators and Technology
Looking ahead, advancements in technology promise to revolutionize how we approach power line insulation solutions. Innovations may include smarter materials that adapt to environmental stresses or enhanced designs that improve efficiency while reducing costs associated with installation and maintenance. As our reliance on electricity grows globally, so too will the demand for high-quality pin insulators that ensure safe transmission across diverse landscapes—ushering us into a new era of energy management.

