Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of electrical transmission, understanding the intricacies of different cable types is crucial for efficiency and reliability. Among these, OPGW (Optical Ground Wire) has emerged as a game-changer in transmission line technology, offering unique advantages over traditional wires. This introduction sets the stage to explore what makes OPGW cable in transmission line applications so vital and how it stands apart from conventional options.
Understanding OPGW and Traditional Wires
To appreciate the significance of OPGW, one must first grasp its foundational elements compared to traditional wires. Traditional earth wires primarily serve as a grounding mechanism, ensuring safety during electrical surges. In contrast, OPGW combines both grounding capabilities and high-speed communication through integrated optical fibers, leading to enhanced functionality in modern infrastructure.
Importance of Transmission Line Technology
Transmission line technology is at the heart of power distribution systems that support our daily lives—from keeping our homes lit to powering industries. As demand for electricity grows and smart grid technologies advance, the need for reliable and efficient transmission methods becomes paramount. This highlights why innovations like OPGW cable in transmission lines are not just beneficial but essential for future-proofing our energy networks.
Overview of OPGW and Its Role
OPGW plays a dual role in modern transmission lines: it provides essential grounding while simultaneously facilitating high-speed data communication between substations and control centers. This capability allows utilities to monitor their systems more effectively than ever before, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime during outages or maintenance activities. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will uncover key specifications of OPGW cable that set it apart from traditional earth wire options while also examining its comparative advantages against other technologies like ADSS cable.
The Basics of OPGW Cable
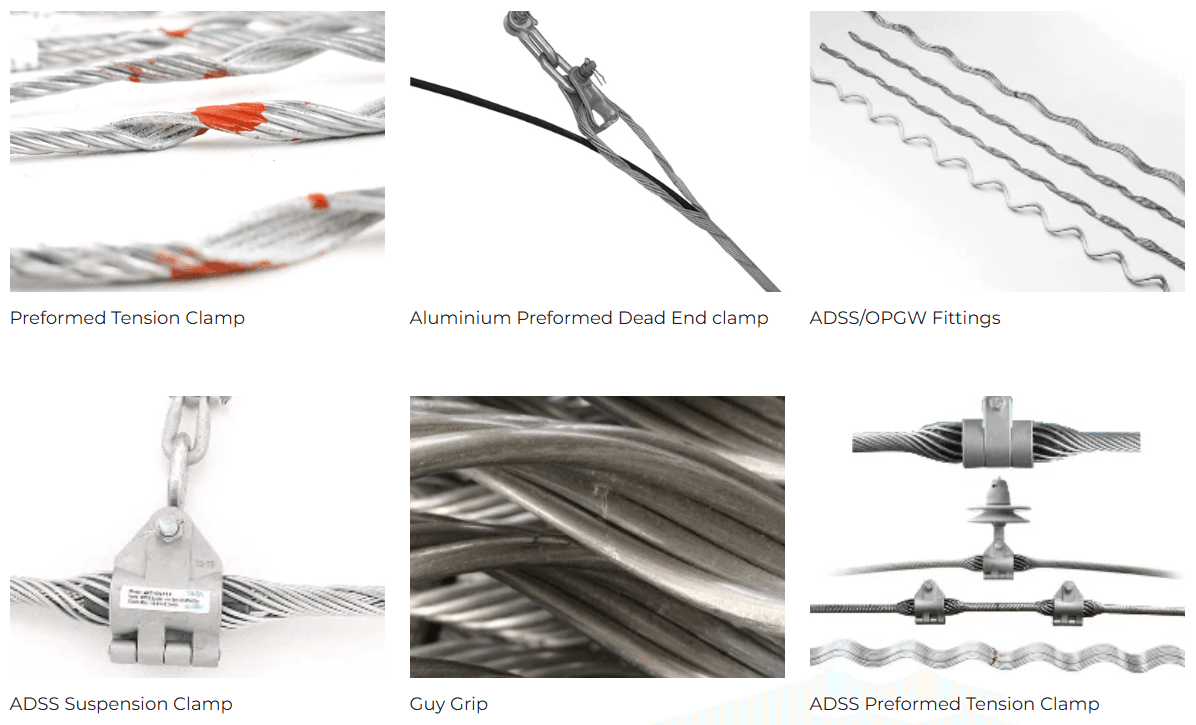
Understanding the fundamentals of OPGW (Optical Ground Wire) cable is crucial for anyone involved in modern transmission line technology. This innovative cable not only serves as a ground wire but also provides high-speed communication capabilities, making it a game changer in the industry. In this section, we’ll explore what OPGW is, its key specifications, and how it stacks up against traditional earth wires.
What is OPGW Cable in Transmission Line
OPGW cable in transmission line systems is a unique hybrid solution that combines the functions of grounding and communication into one efficient design. It typically consists of optical fibers encased within an aluminum or steel wire, providing both strength and data transmission capabilities. This dual functionality allows utility companies to monitor their lines while maintaining safety and reliability.
Key Specifications of OPGW Cable
When discussing OPGW cable specifications, several critical factors come into play, including tensile strength, fiber count, and temperature ratings. The tensile strength ensures that the cable can withstand environmental stresses such as wind and ice loads while maintaining its integrity over time. Additionally, the fiber count determines how much data can be transmitted simultaneously; higher counts allow for more extensive communication networks.
Comparing OPGW with Traditional Earth Wire
What is the difference between OPGW and Earth Wire? Traditional earth wires primarily serve as protective measures against lightning strikes and electrical faults without any communication capabilities. In contrast, OPGW not only provides grounding but also enables real-time data transfer through its embedded optical fibers—making it a superior choice for modern transmission lines.
To visualize these differences effectively:
The Functionality of OPGW

The functionality of OPGW (Optical Ground Wire) is a game-changer in transmission line technology, merging the roles of communication and protection. By integrating optical fibers into the ground wire, OPGW cable in transmission line applications not only safeguards against lightning strikes but also facilitates high-speed data transmission. This dual functionality makes it a vital component in modern infrastructure.
How OPGW Enhances Communication
OPGW enhances communication by providing a robust medium for data transfer alongside existing electrical lines. With its built-in optical fibers, OPGW enables real-time monitoring and control of power systems, significantly improving operational efficiency. This capability is particularly beneficial for utility companies that rely on quick and reliable communication to manage their networks effectively.
Moreover, the integration of OPGW cable in transmission lines allows for seamless connectivity between substations, ensuring that critical information flows uninterrupted. Unlike traditional earth wires that offer no communication capabilities, the advanced design of OPGW transforms how utilities manage their infrastructure. In essence, the enhanced communication features make it indispensable in today's digital age.
OPGW vs Shield Wire: Key Differences
When comparing OPGW vs shield wire, it's essential to understand their fundamental differences and functionalities within transmission lines. Shield wires primarily serve as lightning protection for conductors but lack any communication capabilities inherent to OPGW cables. In contrast, while both protect against electrical surges and environmental factors, only OPGW offers integrated optical fibers for data transmission.
Additionally, what is the difference between OPGW and earth wire? The latter is solely focused on grounding purposes without any added benefits like fiber optics or enhanced communications found in an OPGW setup. Thus, choosing an appropriate solution depends largely on whether you need basic protection or advanced capabilities offered by modern technologies like OPGW.
The Role of Spark Fittings in OPGW
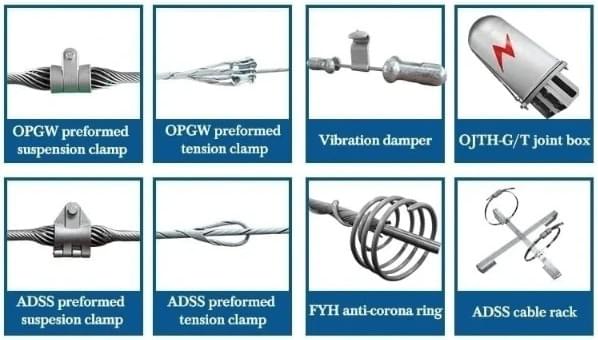
Spark fittings play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and safety of an OPGW installation within a transmission line framework. These fittings are designed to connect the optical ground wire securely to various components while also facilitating grounding when necessary—this is especially important during adverse weather conditions or electrical faults. By providing effective grounding solutions alongside data transfer capabilities through optical fibers, spark fittings enhance overall system resilience.
Furthermore, understanding what is the difference between conductor and OPGW helps clarify why these fittings are vital: conductors transmit electricity but do not support fiber optic connections like those found in an OPGW setup with spark fittings installed properly. This combination ensures that utilities can maintain both power distribution integrity and high-speed communications across their networks seamlessly.
In summary, spark fittings are integral to maximizing the advantages offered by an opgw cable in transmission line applications—ensuring safety while enhancing performance through innovative design features tailored for modern energy demands.
OPGW vs ADSS Cable
When it comes to comparing OPGW and ADSS cables, the differences are as clear as day. OPGW (Optical Ground Wire) integrates both electrical grounding and optical fiber capabilities within a single cable, making it a dual-purpose solution for modern transmission lines. In contrast, ADSS (All-Dielectric Self-Supporting) cable is designed solely for communication purposes and is not meant to carry electrical current or provide grounding.
What is the Difference Between OPGW and ADSS Cable
The primary distinction between OPGW cable and ADSS cable lies in their functionalities. While OPGW serves the dual role of protecting transmission lines from lightning strikes while simultaneously facilitating high-speed data communication, ADSS is purely focused on providing telecommunication services without any grounding function. Additionally, when considering what is the difference between conductor and OPGW, it's essential to note that conductors are primarily designed for transmitting electricity, whereas OPGW combines both electrical grounding and fiber optic capabilities in one package.
Use Cases for OPGW and ADSS in Transmission
In terms of use cases, both cables have their unique advantages depending on the application needs of a transmission line. For instance, OPGW cable in transmission line setups excels in areas where both power delivery and data communication are required simultaneously—think of renewable energy sites or urban infrastructure projects where space is at a premium. On the other hand, ADSS finds its niche in environments where existing structures can support its installation without needing electrical connections or grounding—ideal for long-distance communication links across rural landscapes.
Advantages of OPGW Cable Specifications
The specifications of OPGW cables offer several compelling advantages over traditional solutions like shield wires or even standard conductors. First off, with its robust design integrating optical fibers into an existing ground wire framework, it reduces installation costs by eliminating the need for separate communication lines—this saves time and resources significantly! Furthermore, when discussing what cable is used in transmission lines today, many engineers favor OPGW due to its ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining signal integrity—a critical consideration when evaluating future trends in power line technology.
Size Matters: OPGW Cable in Transmission Line Size
When it comes to the OPGW cable in transmission line applications, size really does matter. The right size ensures that the cable can efficiently handle electrical loads while also providing adequate protection and communication capabilities. In this section, we’ll delve into how to choose the right size for OPGW cables, the factors that influence their dimensions, and some common sizes used in transmission lines.
Choosing the Right Size for OPGW
Choosing the right size for OPGW cables is crucial for optimizing their performance in transmission lines. Factors such as electrical load capacity, environmental conditions, and installation requirements all play a significant role in determining the appropriate dimensions. A well-sized OPGW cable not only enhances reliability but also ensures effective communication alongside power transmission.
In essence, one must consider what cable is used in transmission line setups when selecting an OPGW cable. The specifications of different sizes can vary significantly; thus consulting with manufacturers or engineers is advisable to ensure compatibility with existing infrastructure. Ultimately, a well-chosen size will lead to reduced maintenance costs and improved operational efficiency.
Factors Affecting OPGW Cable Size
Several factors affect the sizing of OPGW cables in transmission lines, making it essential to evaluate each carefully. One primary consideration is load capacity; larger cables can carry more current but may also be heavier and more expensive to install. Environmental factors like wind speed, ice loading on overhead lines, and temperature variations also influence how robust an OPGW must be.
Additionally, understanding what is the difference between conductor and OPGW aids in making informed decisions about sizing requirements based on application needs. For example, while traditional conductors might suffice for basic functions, incorporating an OPGW necessitates additional considerations due to its dual role of carrying electricity and facilitating communication networks within power systems. Therefore, evaluating these factors holistically allows for optimized performance tailored to specific operational contexts.
Common Sizes Used in Transmission Lines
Common sizes of OPGW cables vary widely depending on their intended use within different types of transmission lines. Typically measured by diameter and weight per unit length, these specifications are essential when planning installations or upgrades within existing power grids. For instance, standard sizes often range from 7 mm to 20 mm in diameter—each suited for different voltage levels and environmental conditions.
Moreover, knowing what is the difference between OPGW cable and ADSS cable can help clarify which options are suitable based on size requirements as well as functionality needs like enhanced data transfer capabilities or weather resistance features inherent to each type of cable design. Understanding these common sizes not only streamlines project planning but also helps ensure compliance with industry standards regarding safety and efficiency.
OPGW and Conductors

In the world of electrical transmission, understanding the distinctions between various technologies is crucial for optimal performance. One such technology is OPGW, or Optical Ground Wire, which serves multiple functions in a transmission line setup. This section will delve into the differences between conductors and OPGW, highlighting why OPGW cable in transmission line applications is gaining traction.
What is the Difference Between Conductor and OPGW
The primary difference between a traditional conductor and an OPGW lies in their functionality and design. Conductors are primarily designed to carry electrical current, whereas OPGW combines this function with optical fiber capabilities for communication purposes. In essence, while both are used in transmission lines, an OPGW cable provides enhanced communication features alongside its role as a conductor.
Another critical distinction is that traditional conductors typically lack any protective shielding against environmental factors like lightning strikes or electromagnetic interference. In contrast, OPGWs are designed with integrated optical fibers housed within a protective aluminum layer that also serves as an earth wire. This dual functionality makes it essential to understand what is the difference between conductor and OPGW when considering upgrades to existing transmission infrastructure.
The Benefits of Using OPGW Over Traditional Conductors
The benefits of using OPGW over traditional conductors are numerous and compelling for utility companies looking to modernize their systems. First off, one significant advantage of using an OPGW cable in transmission line setups is its ability to facilitate high-speed data transfer through its embedded optical fibers—something traditional conductors simply cannot do. This capability allows for real-time monitoring of electrical systems, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Moreover, since the OPGW acts as both a ground wire and a communication medium, it reduces the need for additional cabling infrastructure—saving both installation costs and space on existing towers. This dual-purpose nature also means that utilities can streamline maintenance efforts by having fewer cables to monitor and manage over time. As we weigh the pros and cons of different technologies, it becomes increasingly clear that opting for an OPGW cable specification can lead to long-term savings while improving system reliability.
Future Trends in OPGW Cable Technology
Looking ahead at future trends in OPGW cable technology reveals exciting possibilities that could further revolutionize transmission lines. With advancements in materials science, we may see lighter yet stronger designs that enhance the performance of these cables while reducing strain on existing tower structures—a critical factor when considering what cable is used in transmission lines today versus tomorrow.
Additionally, ongoing developments aim to improve data capacity within optical fibers embedded in these cables; this would allow utilities not only to transmit power but also vast amounts of data simultaneously without compromising quality or speed—an upgrade from current standards where bandwidth can be limiting. Furthermore, innovations related to smart grid technologies will likely integrate more sophisticated monitoring systems using advanced sensors built directly into future generations of OPGWs.
As we explore these emerging trends along with existing comparisons like OPGW vs shield wire, it's clear that adopting modern solutions like those offered by advanced versions of optical ground wires will be vital for meeting future energy demands efficiently.
Conclusion

As we wrap up our exploration of OPGW cable in transmission line technology, it's clear that this innovative solution offers numerous advantages over traditional wires. OPGW not only enhances communication capabilities but also provides structural benefits that traditional earth wires simply can't match. With its unique design and specifications, OPGW has established itself as a critical component in modern transmission systems.
Summary of OPGW Benefits
The benefits of OPGW cable are manifold, particularly when considering its dual function as both a ground wire and a communication medium. One major advantage is that it effectively combines the roles of traditional earth wire and fiber optic cables, leading to significant cost savings and efficiency improvements in transmission lines. Additionally, the robust construction of OPGW ensures greater resilience against environmental factors, making it an ideal choice for various terrains.
Final Thoughts on OPGW vs Traditional Wires
When comparing OPGW to traditional wires, the differences become strikingly apparent. For instance, while traditional earth wires primarily serve protective roles, OPGW seamlessly integrates advanced communication capabilities into its design—what is the difference between OPGW and Earth Wire? Simply put: versatility versus singularity. As industries continue to evolve towards smarter solutions, choosing the right cable used in transmission lines will undoubtedly lean more towards advanced options like OPGW.
The Future of Transmission Line Solutions
Looking ahead, the future of transmission line solutions appears bright with advancements in technologies like OPGW cable specifications paving the way for enhanced connectivity and reliability. Innovations are not just limited to performance; they extend into areas such as size optimization—considering what is the difference between conductor and OPGW? This evolution promises to deliver even more efficient systems tailored for specific needs within diverse environments. Furthermore, understanding what is the difference between OPGW cable and ADSS cable will help stakeholders make informed decisions as they navigate this exciting landscape.

